Embarking on the promising journey of mushroom farming? It’s indeed a worthwhile and fruitful endeavour. The mushroom business has grown into a huge market. People cares more about health and natural flavours. We bring to you Promising Mushroom Farming Business: A Profitable Step-by-step Guide

The allure is simple: these delectable fungi are a culinary wonder and a nutritional powerhouse. From Michelin-starred restaurants to humble households. Mushrooms have carved their place on plates worldwide.
Within the folds of this comprehensive guide lies the roadmap. To metamorphose your mushroom aspirations into a thriving reality. Prepare, enlighten yourself, as you’ll uncover the secrets of spore to harvest. Learning the art of profitable mushroom farming business.
Get ready to start into the captivating realm of mushroom farming. A journey that promises financial rewards. The curtain rises on your very own mushroom odyssey.
Also Read:
- Top Agritech Startups Fueling Agriculture Growth in India
- Harvesting Treasure: How to Save Yarsagumba, the Himalayan Viagra
What are Mushrooms
Mushrooms are fungal organisms that belong to the kingdom of Fungi. They are distinct from plants, animals, and bacteria. Mushrooms are well-known for their various shapes, sizes, colours, and textures.

Mushrooms consist of a fruiting body, which is the visible part we recognize. This fruiting body contains spores, the equivalent of plant seeds. When these spores release, they can germinate and give rise to new fungal growth.
Mushrooms are not plants and do not undergo photosynthesis. Instead, they get nutrients through absorption. Mushrooms are fascinating and diverse fungal organisms. They contribute to ecosystems, human diets, and scientific research.
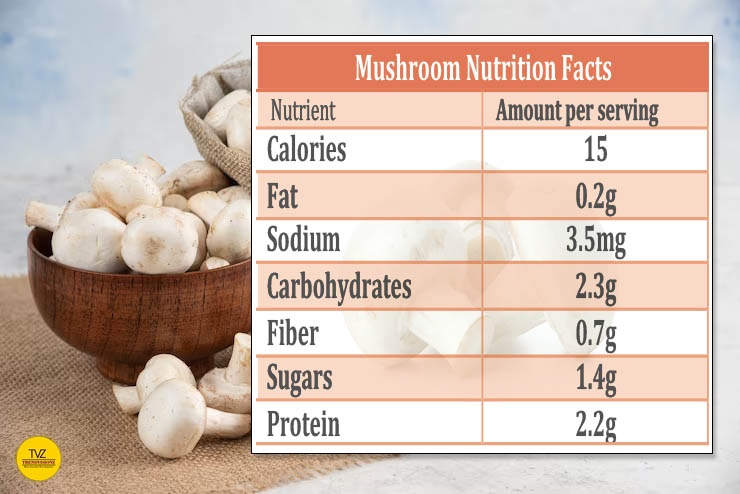
One cup of mushrooms (70g) Source: USDA)
Also Read: Sustainable Azolla Farming: The Future of Protein Livestock Feed
Mushrooms: Nature’s Nutrient Powerhouses
As per studies, there are around 2,786 mushroom species from 99 countries. Out of these, 2,189 are edible species. And only about 30 are cultivated and sold. Mushrooms, often celebrated for their delectable flavours pack a punch of essential nutrients. With notable minerals, mushrooms contribute to a balanced diet. Moreover, they contain antioxidants and dietary fibre, aiding digestion and bolstering immune function.
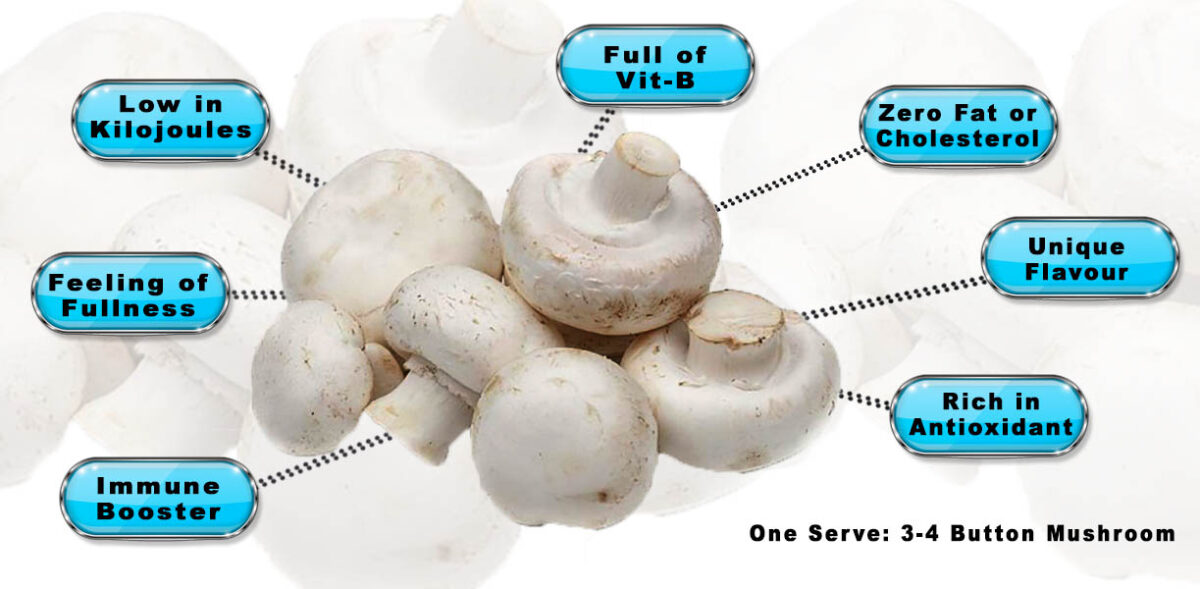

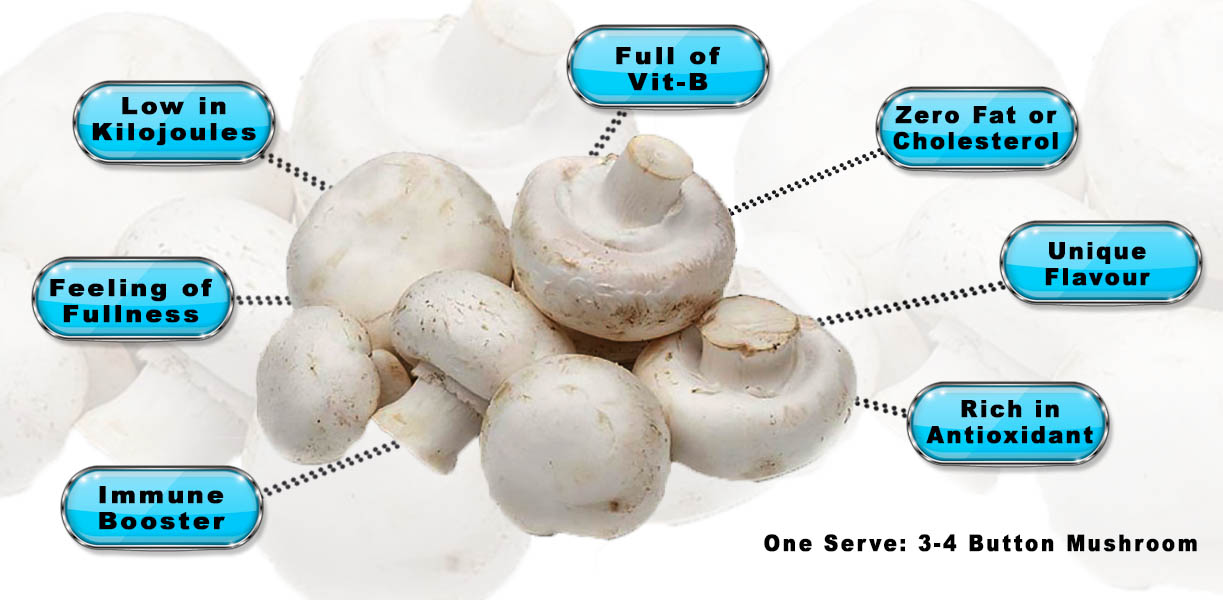
Incorporating mushrooms into your diet can:
- Enhance Nutrient Intake: Mushrooms amplify your vitamin and mineral intake, supporting health.
- Support Digestive Health: The dietary fibre in mushrooms aids digestion and gut health.
- Boost Immunity: Antioxidants like selenium and vitamins help fortify your immune system.
- Provide Low-Calorie Protein: Mushrooms offer a plant-based protein source with minimal calories.
- Promote Heart Health: Potassium and antioxidants contribute to cardiovascular well-being.
As you savour their taste, relish the wholesome advantages. These fungi bring to your plate and well-being. Experience their diverse benefits while enjoying their delightful flavours.
The Booming Mushroom Farming Industry
The mushroom farming industry is booming globally. The demand for mushrooms is growing due to their nutritional benefits and versatility.
According to industry reports, the mushroom market will reach $62.44 billion in 2023. It is growing at a rate of 9.2% per year. China ranks the highest in the mushroom business, followed by Japan and Poland. This huge growth is due to increasing awareness of mushrooms’ health benefits. And also due to growing interest in meat alternatives.
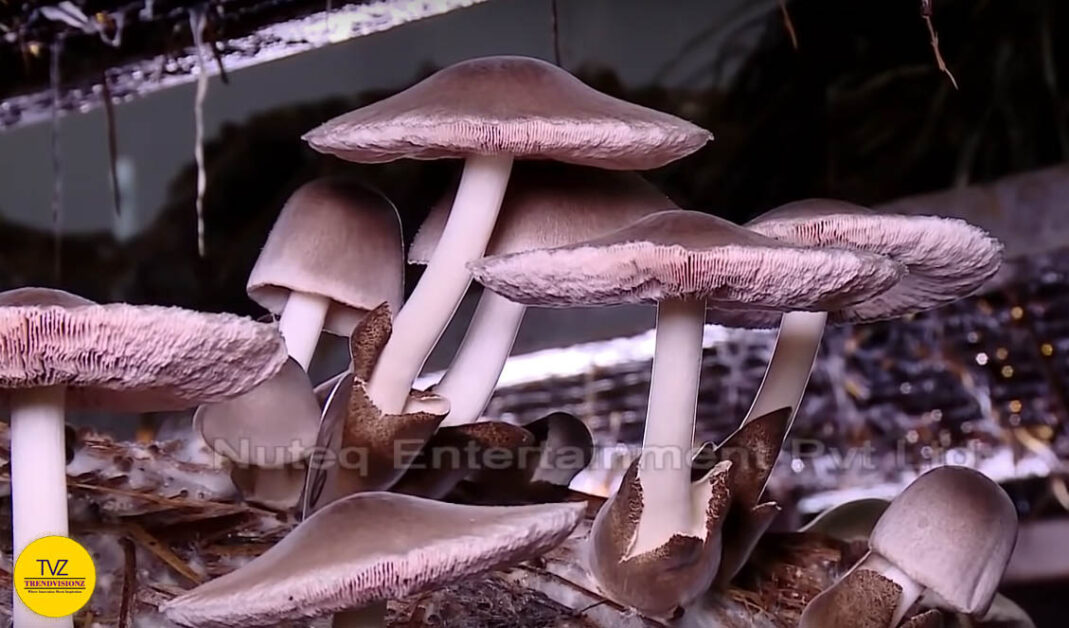

The number of mushrooms eaten in India has increased by more than 250% in the last ten years. India is still an open market, even though it has more than 1.3 billion people, and their salaries are increasing. Growing mushrooms can be a good way to make money. Especially for small and medium-sized businesses.
According to the National Horticulture Board, Bihar grows the most mushrooms. Followed by Maharashtra, Odisha, Haryana, Punjab, and Himachal Pradesh. The mushroom-growing business is on an upward trend in the country. The growing projection presents a lot of opportunities.
Discovering Nature’s Hidden Partnership
Beneath the forest floor and within the intricate networks of plant roots lies a captivating tale of collaboration. That has shaped ecosystems for millennia. Mycorrhizal symbiosis is a remarkable partnership between fungi and plants. It unveils a hidden world of nutrient exchange, resilience, and coexistence.
People have gathered mushrooms from the woods and eaten them as food. About a thousand years ago, the Chinese were the first to grow mushrooms artificially. In the 16th and 17th centuries, Europeans began commercial farming in greenhouses and caves. Farming mushrooms is a good way to make money. They are good for your health. Helping ordinary farmers in more than 100 countries to make money.

Selecting the Right Mushroom Variety for Your Farm: Top Choices
Picking the perfect mushroom variety for your farm is a crucial decision. Choosing which mushroom variety to grow depends on factors like available growing equipment, climate conditions, and your target market. The most common options are:
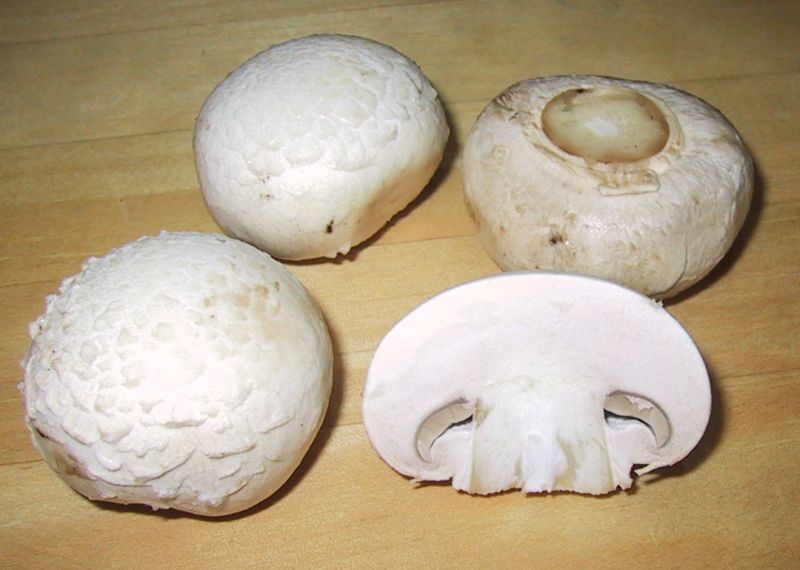
1. Button Mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus):
Also known as white mushrooms or champignon mushrooms. It is the mostly cultivated and consumed mushrooms. About 90% of all mushrooms eaten in the United States are white button mushrooms. They have a mild flavour and a firm texture. Plus, they grow fast and don’t need special conditions. It is one of the best vegetables to grow in pots.

2. Straw Mushrooms (Volvariella volvacea):
These are as popular in India as the Chinese mushrooms or paddy straw mushrooms. They have a good aroma and flavour and are rich in various nutrients and proteins. In the tropics and subtropics, these mushrooms are usually edible. In India, they are grown in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Andra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu and Chhattisgarh.

3. Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus):
Named for their resemblance to oysters. Also called Dhingri in India. These mushrooms are thin and soft and taste mild and slightly sweet. In India, they are most often grown in Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Orissa, Karnataka, Maharashtra, etc.

4. Cremini Mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus):
These are like button mushrooms. Also known as Portobello Mushrooms. They are darker in colour and have a deeper, earthier flavour. They’re also a good step for beginners looking to try something new.

5. Shiitake Mushrooms (Lentinula edodes):
Originating from Asia. It is the most commonly cultivated mushroom in Japan. Shiitake mushrooms have a distinctive smoky and meaty flavour. They take a little longer to grow and prefer hardwood logs.

6. Maitake Mushrooms (Grifola frondosa):
Also known as hen-of-the-woods. Maitake mushrooms have a strong, earthy flavour. They are often used in Japanese and Chinese cooking. Theu have high value for their potential health benefits.

7. Enoki Mushrooms (Flammulina velutipes):
These mushrooms have long, thin stems and small caps. They have a mild, fruity taste and is use in salads, soups, and Asian dishes.

8. Chanterelle Mushrooms (Cantharellus cibarius):
Chanterelles have a vibrant golden colour. And a unique, fruity aroma. They have a delicate, peppery flavour. Are considered a gourmet delicacy.

9. Morel Mushrooms (Morchella spp):
Morels have a distinctive appearance with their sponge-like caps. They have an earthy, nutty flavour and are sought after by chefs and foragers.

10. Porcini Mushrooms (Boletus edulis):
These mushrooms have rich, nutty flavour. Italian and Mediterranean cuisines often use them. One can find them both wild and cultivated.

11. Reishi Mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum):
Known for their potential medicinal properties. They are also called Lingzhi or Reishi mushrooms and are often used in teas and supplements. They have a bitter, woody taste. Oriental Fungus has been used for a long time in China, Japan, and other Asian countries to help people stay healthy and live longer.

Consider your space, time, and preferences when picking a variety. Starting with options like Oyster or White Button mushrooms can be smart. As you gain experience, you can venture into more adventurous choices.
Happy growing, and enjoy your delicious harvest!
Have you read this? 20 Most Popular Cows Of Indian Breed: The Divine Dairy Herd
Setting Up Your Mushroom Farm: Cultivation Process
It would help to gather essential equipment and set up an ideal growing environment to get your mushroom farm up and running.

Requirement of Typical Mushroom Farm
Choose the right equipment and environment for your chosen mushroom. Start with inoculation and cultivation. Do your research to determine the specific needs of each mushroom species. An important exercise for a Promising Mushroom Farming Business
Growing Medium
Mushrooms need a moist, sterile medium to grow in. The most common are straw, sawdust, corn cobs, cottonseed hulls, and composted manure. Choose a medium suited to the mushroom species you want to cultivate. Moisten the medium before inoculating with mushroom spawn.
Spawn
Mushroom spawn contains the mycelium. These are mushroom roots that will colonize your growing medium. Buy spawn from a reputable supplier to ensure high quality and viability. Different mushrooms need different spawn types. So choose based on the species you want to grow.
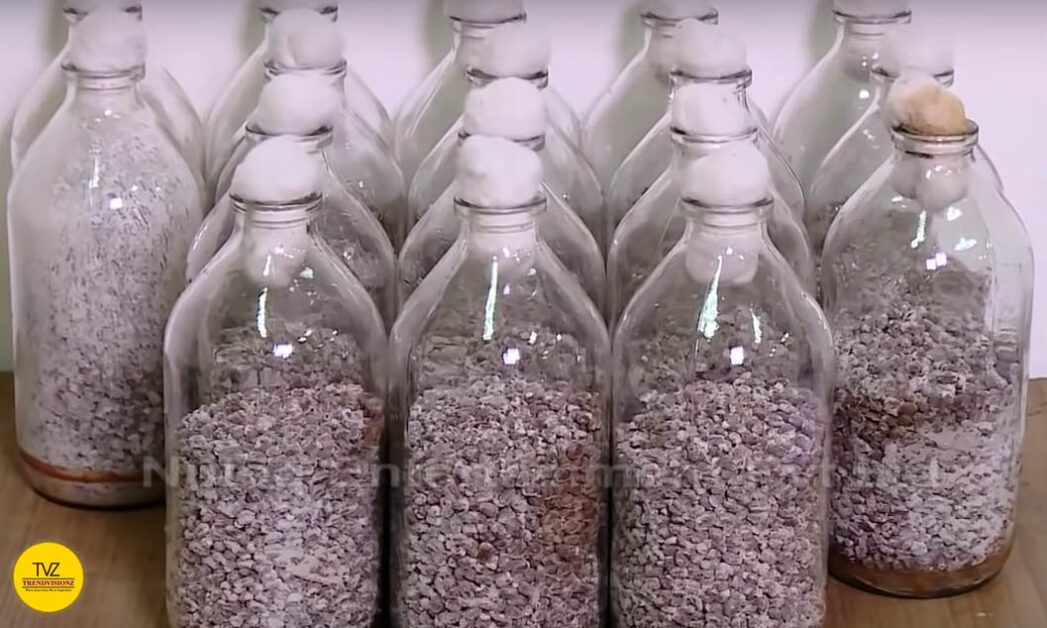

Humidity and Temperature Control
Mushrooms need warm and humid conditions to thrive. You’ll need equipment to watch and control temperature and humidity. Equipment like thermostats, humidifiers, air conditioners, and ventilation fans.
Containers
You’ll need containers to hold the inoculated growing medium during spawn run and fruiting. Trays, bags, bottles, and other containers should have holes or filters. To allow air exchange while keeping contaminants out. Sterilize all containers before use to ensure the best results.
Lighting
Some mushroom species need light to stimulate pinning and fruiting. Provide artificial lighting on a timer for 12-16 hours per day. The intensity and duration will depend on the mushroom type.
Essential Components of a Mushroom Farm: Building Blocks of Success
A profitable mushroom farming demands a planned arrangement of critical components. Each of which plays an important part in the cultivation process. From composting to post-harvest processing. Here’s a look at the essential elements of a thriving mushroom farming business:

Composting and Substrate Preparation:
- Composting Unit
- Outdoor Phase-I Composting Platform/Indoor Bunkers
- Indoor Phase-II in Peak Heating/Bulk Past-Chamber
- Peak Heating Chamber
- Bulk Pasteurization Chamber
- Casing Pasteurization Chamber
- Cooling Solutions for Summer
Spawn Production:
- Spawn Unit
- Spawn Laboratory
Cropping Infrastructure:
- Seasonal Cropping Rooms
- Environment-Controlled Cropping Rooms
- Environment Control, Air Conditioning, and Air Circulation
Ancillary Units:
- Post-Harvest Handling Unit
- Pre-Cooling Chamber
- Canning Hall with Canning Line
- Packaging Room
These elements work together to form a cohesive and effective mushroom farming ecology. Understanding how to orchestrate these components assures ideal growing conditions. Increases productivity, and quality. Thus pushing your mushroom farm towards a wealthy future.
Crafting the Foundation: Mushroom Compost Preparation

Compost preparation is the most important part of growing mushrooms. Organic materials like straw, chicken litter, and gypsum is mix to make a nutrient-rich ground.
Preparation of Phase-I starts the microbial activity. This turns raw ingredients into a healthy material. Phase-II refines the mix, eliminating germs and making a good place for mushrooms to grow.
Mushroom compost requires some expert-guided steps. This sets the stage for strong mycelium colonization and, eventually, a plentiful crop.
Every details from the raw materials to the alchemy of fungi.
Selection and Preparation of Substrate for Mushrooms
Choosing the right mushroom substrate can make or break any mushroom-growing project. Growing mushrooms on a substrate is somewhat like growing plants in soil. Different species of mushrooms prefer other substrates.
A mushroom substrate is a medium that allows mushroom mycelium. This is the vegetative part of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching threads called hyphae. To develop and establish itself. The substrate offers mushrooms the nutrition. And the moisture, and energy they need to grow and fruit.
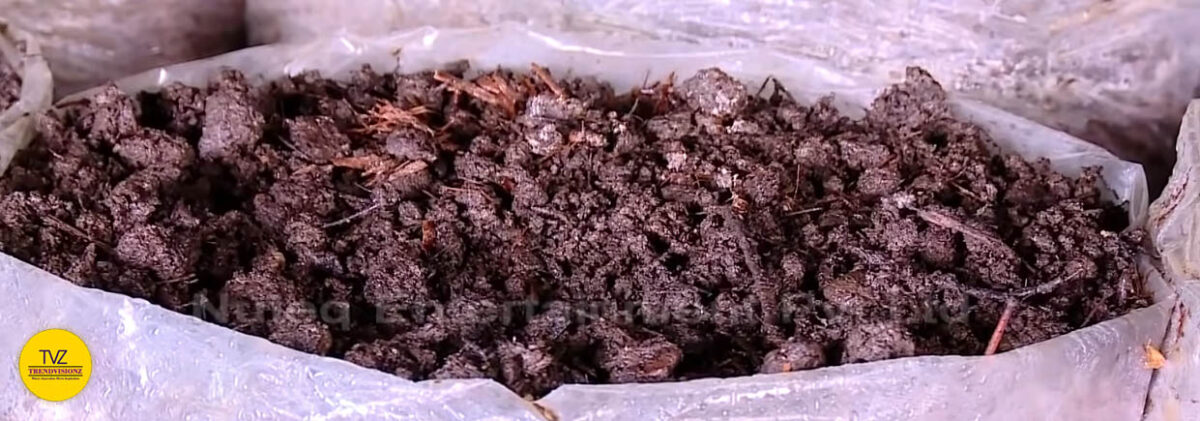

Selecting the best substrate comes down to a few factors. The first thing to consider is the availability and ease of working with a particular substrate. For example, a straw-based substrate may be far more accessible than a hardwood substrate. We would suggest that you select a substrate that is available in your area. It would help if you also chose your substrate to match the species of mushrooms you are growing.
Nurturing Mushroom Seed Production: Cultivating the Key to Abundant Harvests
Learn about mushroom seed production. This is a key step that sets the stage for a successful growing trip. The complicated method includes making pure cultures of mycelium.
What is a Mushroom Spawm?
Mycelium, the live culture of fungi, grows on a medium to make spawn. It is the backbone of any business that grows mushrooms. Think of it as the mushroom seeds you need to start a farm.
The process of Spawm Production ensures the purity and strength of the genes. By learning how to produce Mushroom seeds, you can control your mushroom crops’ quality, quantity, and regularity. Find out how to grow Mushroom as you take this important step towards rewarding yields.
Join Over 1M Viewers in Exploring the Fascinating World of Mushrooms.
Cultivating Mushrooms: 10 Step-by-Step Guide
Once your spawn and substrate are ready, it’s time to grow! Here are the basic steps to cultivate your mushrooms:
- Fill your container with the substrate. For oyster mushrooms, use straw or hardwood sawdust. For shiitake, use hardwood sawdust or logs. Pack the substrate. But not too tight.
- Make holes or slits about 6 to 8 inches apart in the substrate. For sawdust blocks, make holes with a dowel. For straw, make slits with a knife. For logs, drill holes with a drill bit.
- Inoculate the holes or slits with spawn. For sawdust blocks, insert spawn-filled dowels into the holes. For straw and logs, insert spawn into the slits and holes. Seal the openings with wax or cheesecloth and twine.
- Incubate the inoculated substrate in a humid environment. For sawdust blocks, please place them in a plastic bag in indirect light. For logs, stack them in a shady area. Maintain humidity and temperatures of 65 to 72 F.
- Check for full colonization of the substrate by the mycelium. This can take 4 to 12 weeks. The substrate should become firm and white. Break it open to check inside.
- Once colonized, move the substrate to a fruiting chamber. Humidity should be 85 to 95%. And temperatures of 50 to 65 F. Fresh air exchange is important for fruiting.
- Continue to maintain humidity and temperatures. Misting and fanning the substrate 2-3 times daily will stimulate mushroom growth.
- Harvest mushrooms once the caps have opened. Cut them off at the base. Do not pull them out.
- After the first harvest, continue to mist and fan as new mushrooms will form. You can usually get 2-3 crops from a single injection.
- Start the process over to continue cultivating more mushrooms! With practice, you’ll be harvesting pounds of mushrooms in no time.
Unveiling the Profit Potential: Mushroom Farming Economics
Mushroom farming requires an initial investment. It can be quite profitable if done right. You’ll need a climate-controlled growing room. And containers, substrate, spawns, and other equipment to get started.
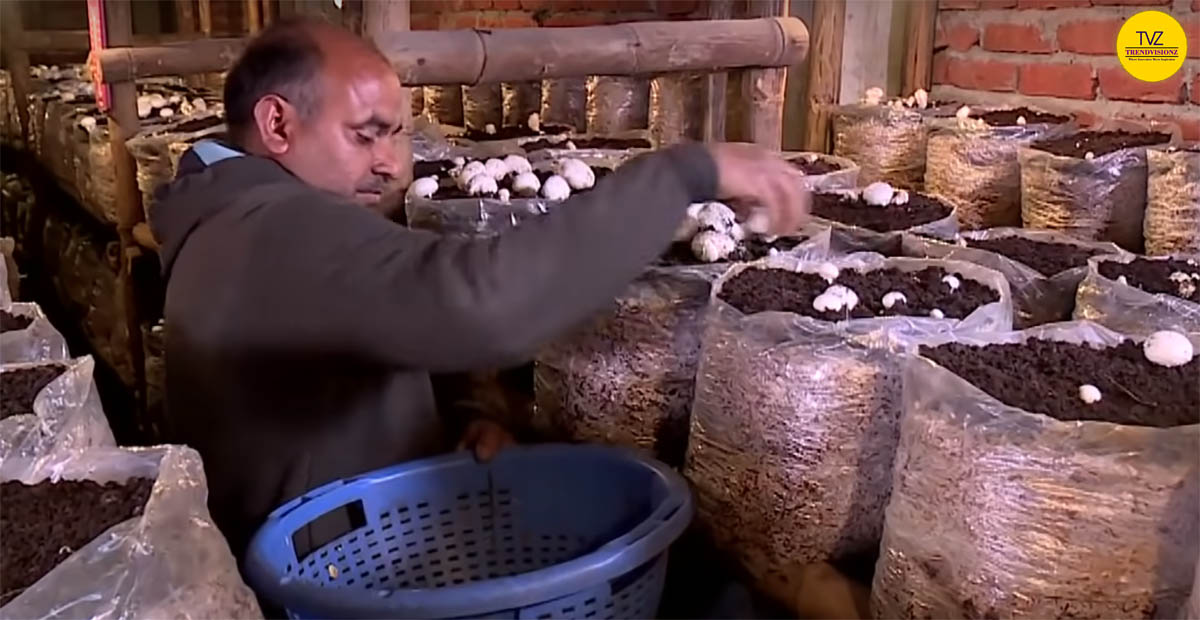

Growing gourmet mushrooms like oyster, shiitake or lion’s mane can provide high returns. They often sell for higher prices. Many small mushroom farms can turn a profit within a year. And as your operation grows, costs decrease. As you’ll already have the infrastructure and experience. Some mushroom farmers make $50,000-$100,000 yearly or more from a modest-sized operation. With care and patience, you’ll be well on your way to success in this promising industry.
Harvesting Success: The Cost and Profit Dynamics
Embarking on a journey into mushroom farming’s financial landscape reveals promising horizons. With the price of 1 kg of button mushrooms ranging from ₹140 to ₹165, the potential for profitability beckons.
Cost & Profit Analysis for Mushroom Farming
| S. No | Item | Costing |
| Price of 1 kg of Button Mushroom | ₹140-₹165 | |
| Total cost of 2,500 kgs of button mushroom @₹140 | ₹3,50,000 | |
| Mushroom Farming Total Recurring Cost | ₹1,60,000 | |
| Annual Profit from Mushroom Farming (On an Average) | ₹1,90,000 |
Verdict: Growing mushrooms is a good way to make money
Profit margins in mushroom farming are quite high. You can expect to earn ₹5 to ₹10 per kilogram of mushrooms sold. A small 100-square-foot growing area can produce up to ₹25,000 mushrooms per month. As your business grows, you can make ₹3 to 5 lakhs monthly. The key is keeping costs low and producing a consistent and high-quality product.

Cultivating Profitability: The Verdict
The numbers paint a compelling picture: mushroom farming in India promises to be lucrative. The calculated profit margin reflects the potential to recoup investments. Enjoy large earnings. As the demand for mushrooms continues to rise. The cost-analysis balance tips. Achieving commendable profits in the mushroom farming realm seems attainable.
Exploring Lucrative Avenues: Where to Sell Your Mushroom Harvest
Navigating Sales Channels for Mushroom Farming Success
Embarking on a mushroom farming venture holds immense potential, but the key lies in finding the right market for your harvest. Consider these strategic avenues to showcase your mushroom bounty:
1. Restaurants and Culinary Delights
It’s rising popularity as a healthy, flavourful ingredient has made eateries eager consumers. Collaborate with local restaurants to provide fresh, quality mushrooms that elevate their dishes.
2. Farmer’s Markets
The surge in vegetarian and local food trends has paved the way for mushroom marvels at farmer’s markets. Capitalize on Urban Epicentre of Freshness
3. Online Convenience
Digital platforms like Farmsnation offer a hassle-free way to connect. Your mushrooms with eager consumers seeking quality produce. Leverage the power of e-commerce to local impact and reach a broader customer base.
4. Dried Creations
Transform surplus or imperfect mushrooms into premium dried delights. Capture the niche market for intense flavours. Offer dried mushrooms suitable for export.
5. Gourmet Creations
Craft mushroom-based gourmet products, from sauces to seasonings. Capitalize on adventurous palates. These are high-quality offerings that command a premium.
Seize the opportunity to flourish in the mushroom market. Align your produce with the right sales channels. This strategic approach ensures profitability. And establishes your mushroom farming venture as a thriving success.

Mushroom Farming at Home
Mushroom farming at home is easier than you might think. All you need to get started is a small space like a basement, garage, or shed and the right supplies.
First, get mushroom spawns or cultures. Inoculate your mushroom-growing medium to grow mushrooms at home. Popular and easy varieties for beginners include oyster and shiitake mushrooms. Next, prepare your growing medium. Mushrooms like to expand on straw, hardwood sawdust, corncobs or straw. Soak the medium in water and drain it so it’s damp but not soggy.
Then, load the spawn or cultures into your damp medium. Seal the container and store it in a cool, dark place while the mycelium colonizes the medium. This usually takes 10 to 30 days. Once occupied, open the container and provide light and fresh air circulation. Mist with water to maintain dampness.
Within a week or so, you should see mushrooms forming. Harvest them once the caps start to flatten out. Twist or cut them off at the base.
After harvesting, soak the medium again, and new mushrooms will continue to grow. A single injection of spawn can produce mushrooms for 2-3 months.
Homegrown mushrooms will be more flavourful and nutritious than store-bought. Selling excess mushrooms can turn your hobby into a profitable micro-business.
Some Uses of Mushroom: Recipes
Mushrooms are versatile and lend themselves well to many recipes. Here are a few ideas to get you started:
Soups and Stews
Mushrooms add a savoury umami flavour to soups and stews. Sauté some mushrooms with onions and garlic, then add to chicken noodle soup, beef stew, or vegetable soup. Mushroom soup is also a classic, made from mushroom stock and cream.
Pasta
Toss sautéed mushrooms with pasta such as fettuccine alfredo or mushroom carbonara. Mushrooms pair well with creamy and cheesy pasta dishes. You can also make mushroom pasta sauce to toss with your favourite pasta.
Risotto
Mushrooms are a key ingredient in mushroom risotto, Arborio rice, parmesan cheese, and vegetable stock. Sautéing the mushrooms first helps bring out their flavour before adding to the risotto.
Omelettes and Scrambles
For breakfast, add sautéed mushrooms to omelettes, scrambles, and frittatas. Mushrooms provide a savoury counterpart. To sweet ingredients like bell peppers, tomatoes, spinach and cheese.
Pizza and Flat breads
Top pizza, flatbread, naan or lavash with sautéed mushrooms, mozzarella cheese and fresh or sun-dried tomatoes. Mushrooms pair great with the tangy, herby Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine flavours.
Creamy Mushroom Risotto with Millet
Delight in creamy mushroom risotto, enhanced with wholesome millet for a delectable and nutritious culinary experience. Perfect comfort food
Sandwiches and Burgers
Grilled mushrooms are delicious on sandwiches, burgers, and panini. Brush grilled mushrooms with garlic herb butter or olive oil. Serve them on a burger with Swiss cheese or a sandwich with roasted red peppers and pesto.

Some FAQs: Promising Mushroom Farming Business
So, you have some questions about getting into the mushroom farming business. No worries, that’s understandable—it is a complex undertaking.
Do I need any special skills or training?
No. While a background in agriculture, botany or mycology can be helpful, anyone can learn mushroom farming. The key is following a proven process and gaining hands-on experience. Many online video tutorials and training courses are available to teach you the fundamentals.
How much space do I need?
Mushroom farming does not need a lot of space. You can start with a small garage, shed or basement area. As your business grows, you may need up to 1,000 square feet for a small commercial operation. The space must be humidity and temperature controlled.
Conclusion
So there you have it, a comprehensive guide to starting your own mushroom farming business. While it may seem daunting, if you follow the steps outlined, you’ll be well on your way to success. The demand for mushrooms will only increase, so now is the perfect time to start. Roll up your sleeves, get your hands dirty, and watch your mushrooms and profits grow. Before you know it, you’ll have a thriving business contributing to meeting the rising global demand for this superfood. The opportunities in this industry are endless. What are you waiting for? Get out there and start cultivating your future in mushroom farming today!
Our Digital Imprints:
Get Connected to us on Linkedin- “Transforming Lives“. Creating the magic. Just – Believe ~ Practice ~ Perform
Bonus- Watch Our 7 Steps to Goal Setting on Youtube Videos NuteqEntertainment
Don’t miss out on our most recent resources and recommendations. Join Trendvisionz online magazine today by subscribing!
Get connected to TRENDVISIONZ to stay updated with latest information. All take time out to check our About Us Page. Incase you want to get in touch with us do Contact us. A shoutout to Guest writers.


