Did you know that 94% of large businesses are fuelling their growth, efficiency, and agility? Being ahead of the curve is essential in the digital age we live in today. Different Types of cloud services are the key to unveiling these cloud computing advantages
While terms like “cloud computing,” “IAAS,” and “SAAS” might seem complex. This guide aims to demystify them. We will share clear explanations and practical examples. You’ll gain the knowledge and confidence to leverage the cloud technology.

Understanding the different cloud service models can feel overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify what is a cloud and empower you to leverage its potential.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of cloud computing platforms for businesses. Also, provide examples of cloud computing to illustrate why many are making the shift. In the course of the journey, we will also present some case studies. Successful implementation would be a learning ground.
By the end, you’ll gain a clear understanding of what is cloud computing. This article will delve into explaining the cloud and how it can benefit your business in practical ways. Cloud platforms enable businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently. So, unlock the power of the cloud and embark on a journey towards successful growth.
Also Read:
- 7 Proven Skills to Help You Cope with Stress Successfully
- Timeless Charm: How Bollywood Actresses Are Impacting Brand Endorsement
- India’s EV Evolution: Seize the Moment with Profitable Business Models
Indian Cloud Computing Market Growth
Cloud computing benefits businesses enabling them to innovate, grow, and adapt to changing needs efficiently. Forecasts state that by 2027, the Indian public cloud services industry would be worth $17.8 Bn. Exhibiting a 22.9% compound annual growth rate, or CAGR, between 2022 and 2027.
Public cloud services in India have evolved beyond cost savings and flexibility. Enterprises are investing in modernizing applications, developing cloud-native solutions, and exploring artificial intelligence.
Rajiv Ranjan, Associate Research Director, Cloud and Artificial Intelligence, IDC India.

Enterprises are investing in GenAI, chatbots, and conversational AI tools. It is imperative to know that cloud systems are essential for hosting and managing these advanced AI applications. Cloud platforms facilitate the integration and deployment efficiently. GenAI tools are particularly useful for cost optimization, application development, and workload testing. In the future, GenAI is expected to play a larger role in cloud technology. Be it cloud security or infrastructure management. Driving growth in India’s public cloud services market.
Understanding the Basics: What is a Cloud?
Cloud computing delivers on-demand computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, and software, over the Internet. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are some cloud platform that provide the infrastructure for delivering these services efficiently. Cloud computing advantages enables faster innovation, flexible resource allocation, and cost savings.

Imagine accessing powerful computing resources, storage, and software on demand. Without managing servers and hardware. That’s the magic of cloud computing. Cloud systems provide powerful computing resources, storage, and software on demand, revolutionizing business operations. Unlike traditional on-premise IT, where everything resides in your office.
Cloud is about how you do computing, not where you do computing
Paul Maritz, VMware CEO
The cloud delivers these resources over the Internet, like renting instead of owning. This means scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency for businesses of all sizes. Think of it as using electricity. You pay for what you use, eliminating expensive upfront investments.
Explaining the Cloud
The cloud can be thought of as a vast network of interconnected servers. All located in data centers around the world. These servers hold your data, run applications, and deliver services. Instead of having your own physical servers and hardware on-site. You access these resources over the Internet, like you access a website.
Examples of Cloud Computing in Action
Cloud computing is ubiquitous in modern business operations, offering solutions to various challenges. Examples of cloud computing include cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud.
These services offer a range of cloud computing solutions, including infrastructure services, cloud platform services, and software services, allowing businesses to access computing resources on-demand without the need for physical hardware or infrastructure.

Here are real-world examples of businesses leveraging cloud computing in their daily operations:
- Storage and Backup. Businesses use Amazon Web Services (AWS) to store and back up vast amounts of video content. AWS offers scalable storage solutions that ensure data accessibility and protection.
- Business Applications. Salesforce is a prime example of a cloud-based CRM platform worldwide. It offers improved accessibility, allowing users to manage customer relationships from anywhere, anytime.
- Data Analytics and Business Intelligence. Coca-Cola utilizes Google Cloud’s analytics and AI tools to gain insights from data. This enables them to make data-driven decisions for marketing, sales, and operations.
- Software Development and Testing. Airbnb utilizes cloud services like AWS to develop and test new features on its Platform. This allows them to innovate and scale their services based on demand.
- Streaming Media. Spotify relies on Google Cloud Platform (GCP). To deliver music streaming services to millions of users worldwide. GCP’s scalability ensures smooth playback and minimal downtime.
These examples show the diverse applications of cloud computing across various industries. Showcasing cloud computing benefits in enhancing efficiency, scalability, and innovation in business operations.
The Transformative Power: Benefits of Cloud Computing
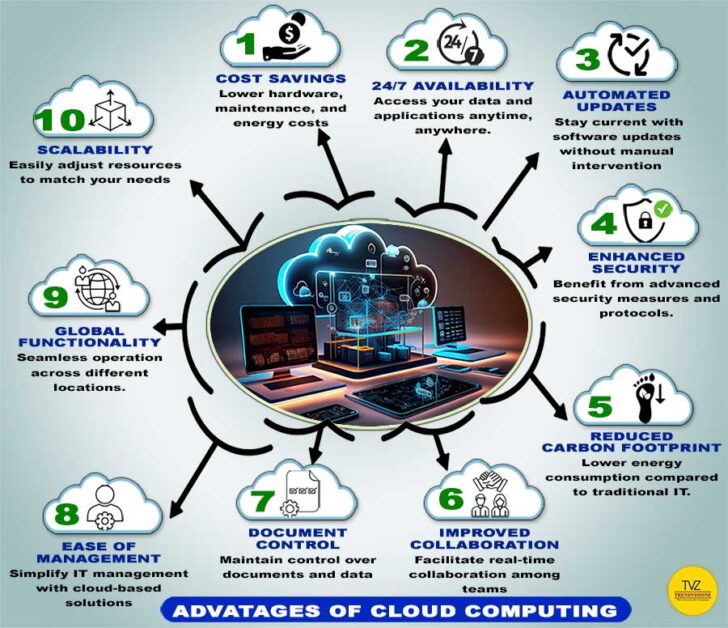
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate. Explaining the cloud offers a multitude of benefits that drive growth, efficiency, and resilience. Cloud computing offers numerous benefits to businesses, making it a popular choice for modern operations.Here are 10 Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost Savings: Reduce hardware, maintenance, and energy costs.
- 24/7 Availability: Access data and applications anytime, anywhere.
- Scalability: Easily adjust resources to match your needs.
- Global Functionality: Operate seamlessly across different locations.
- Automated Updates: Stay current with software updates automatically.
- Enhanced Security: Benefit from advanced security measures and protocols.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Lower energy consumption compared to traditional IT.
- Improved Collaboration: Enable real-time collaboration among teams.
- Document Control: Maintain control over documents and data.
- Ease of Management: Simplify IT management with cloud-based solutions.
Embrace the advantages of cloud computing and unlock a world of possibilities for your business! To harness these benefits and align with specific needs. Overall, cloud computing simplifies IT management, offering a range of benefits for businesses of all sizes. Understanding the different cloud types is crucial.
Understanding the Types of Cloud Computing Models
Cloud computing has evolved into various models. Each offering unique benefits and use cases. Here, we explore the four main types of cloud computing:
1. Private Clouds
Private clouds are dedicated cloud environments for a single user or group. Often behind a firewall. They are host on-premise or in a vendor-owned data center. Offering isolated access and control.
Private Cloud Example: A company hosts its customer data and applications on a private cloud. To ensure data security and compliance.
2. Public Clouds
Cloud environments where the infrastructure is owned & managed by a third-party. They offer services to many tenants and are accessible over the Internet.
Public Cloud Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a range of cloud services. Including computing power, storage, and databases, to businesses worldwide.
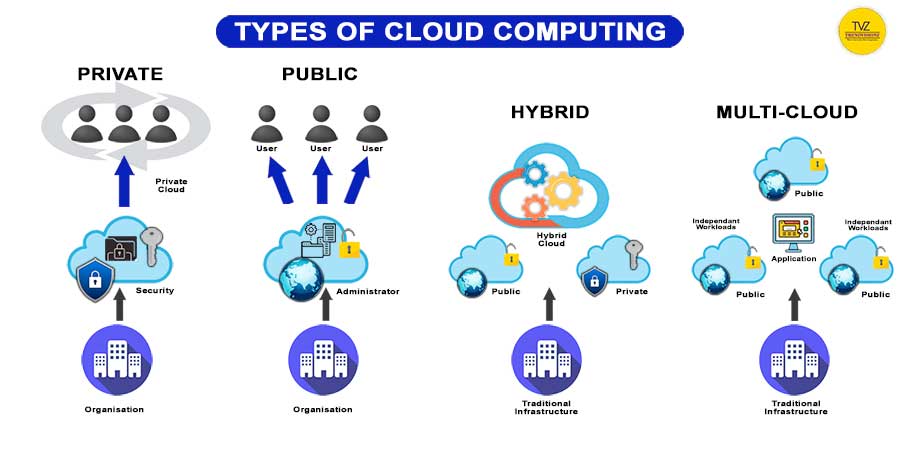
3. Hybrid Clouds
Combining of public and private cloud environments. Hybrid clouds enable the sharing of applications and data across them. This offers the benefits of both environments, such as scalability and security.
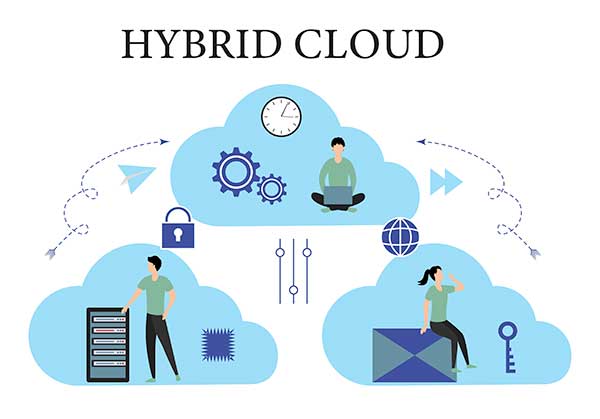
Hybrid Clouds Example: A company uses a private cloud for sensitive data. And a public cloud for less sensitive applications. Achieving a balance between security and flexibility.
4. Multi-Clouds
Multi-clouds refer to the use of many cloud services from different providers. Either public or private. This approach offers redundancy, flexibility, and the ability to choose the best services.
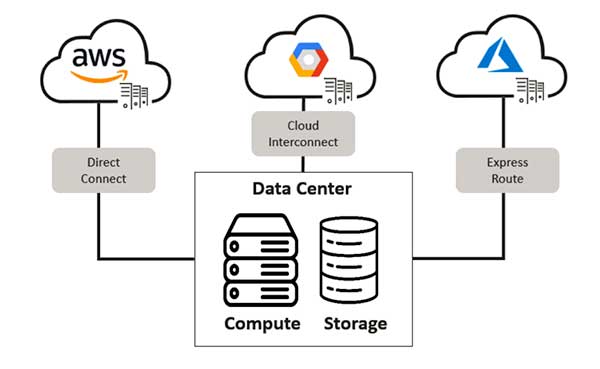
Multi-clouds Example: A company uses Google Cloud for data analytics,. AWS for storage. And Microsoft Azure for machine learning, leveraging the strengths of each provider.
Understanding the different types of cloud computing lays a foundation. Examples of cloud computing showcase its transformative impact on businesses. Helping us explore how we deliver and use cloud services. Let’s now delve into the various types of cloud services to gain a deeper insight into cloud computing.
Exploring the Cloud Service Models
Navigating the world of cloud computing can feel overwhelming. The concept boils down to choosing the right types of cloud services model for your specific needs. The article explores in-depth, the service models of cloud computing
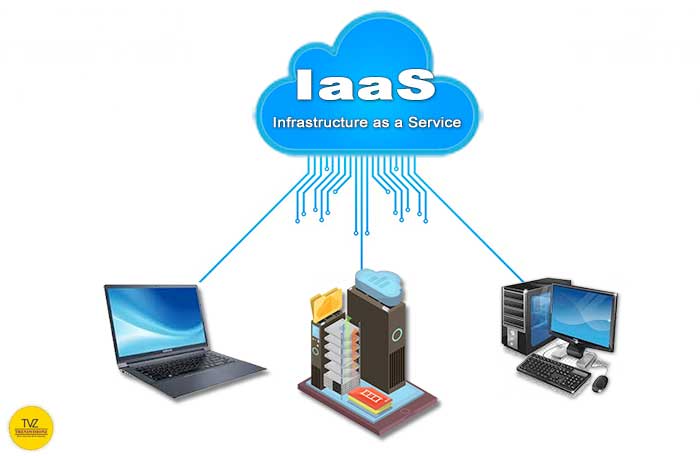
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Definition. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the foundational layer cloud computing model. The third-party provider hosts and manages infrastructure components. Such as servers, storage, and networking. These resources are available for pay-as-you-go rental to users.
How it Works. Users access and manage the infrastructure components through a web-based interface or API. The provider handles maintaining the physical hardware and virtualization layer.
Characteristics:
- On-demand resources: Users can scale resources up or down based on their needs.
- Virtualization: Infrastructure is abstracted from physical hardware, allowing for efficient resource use.
- Self-service: Users can provision and manage resources without human intervention.
- Network connectivity: IaaS providers offer networking capabilities, including firewalls and load balancers.
Benefits:
- Cost-effective: Users only pay for the resources they use, avoiding upfront capital expenses.
- Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down to meet changing demands.
- Flexibility: Users can choose from a variety of operating systems and software.
- Disaster recovery: IaaS providers often offer built-in backup and recovery options.
Drawbacks:
- Security concerns: Users must trust the provider to secure their data.
- Dependency on provider: Users rely on the provider for infrastructure availability and performance.
Uses:
- Development and testing. IaaS provides a cost-effective environment for testing applications.
- Website hosting. Websites can be hosted on IaaS platforms for scalability and reliability.
- Big data analytics. IaaS can provide the computing power and storage needed for big data processing.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers include DigitalOcean, Linode, Amazon Web Services (AWS). Besides Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Rackspace, and Cisco Metacloud. These providers offer scalable and flexible infrastructure solutions for various business needs.
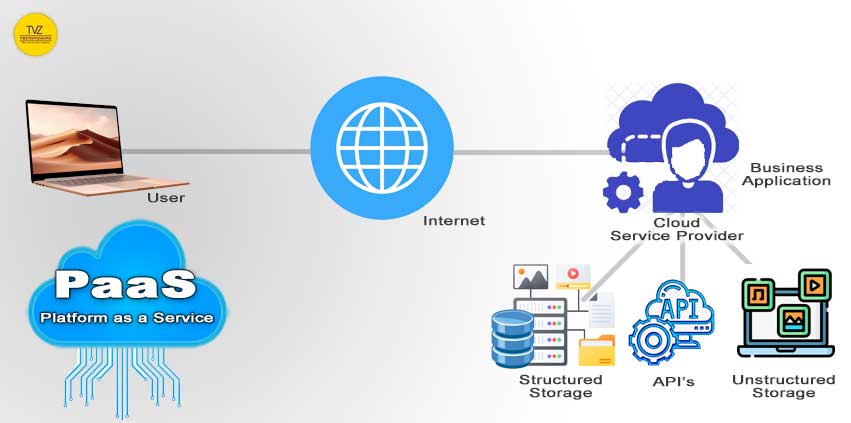
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Definition: Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides the platform in the cloud computing model. It offers a platform so users may create, execute, and maintain apps. Without having to deal with the hassle of constructing and managing the infrastructure. That is usually involved in app development and launch.
How it Works. PaaS providers offer a platform with tools and services. They help develop, test, deploy, and manage applications. Users access these tools through a web-based interface or API. Allowing for streamlined development and deployment processes.
Characteristics:
- Development tools: PaaS platforms provide tools for coding, testing, and debugging applications.
- Scalability: PaaS platforms can scale resources based on application demand.
- Multi-tenancy: PaaS platforms support many users sharing the same infrastructure and development tools.
- Integration. PaaS platforms offer integration with other services. Such as databases, messaging queues, and storage.
Benefits:
- Quicker delivery to market: PaaS expedites the deployment and development of applications.
- Cost-effective: PaaS reduces the need to invest in infrastructure and maintenance.
- Scalability: PaaS platforms can scale resources to accommodate growing application demands.
- Simplified development: PaaS provides pre-built components and tools, simplifying development processes.
Drawbacks:
- Limited control: Users have limited control over the underlying infrastructure.
- Dependency on provider. Users rely on the PaaS provider for platform availability and performance.
Uses:
- Web application development: PaaS platforms are ideal for developing and deploying web applications.
- Mobile application development: PaaS provides tools for developing and deploying mobile apps.
- API development. PaaS platforms helps develop and manage APIs for integration with other services.
Examples of PaaS providers include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure. Besides Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine. And also Apache Stratos, Magento Commerce Cloud, and OpenShift. These platforms offer developers the tools and environment needed. Developers build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexity of managing infrastructure.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Definition: Software as a Service (SaaS) is the top layer in the cloud computing model. Software delivery is over the Internet on a subscription basis. Users do not need to install or maintain the software on their own devices. They access it through a web browser.
How it Works. SaaS providers host and manage the software and its underlying infrastructure. Users access the software through a web browser. And the provider handles maintenance, updates, and security.
Characteristics:
- Accessibility: Any device with an internet connection may access SaaS apps.
- Subscription-based pricing: Users pay a recurring fee for access to the software.
- Automatic updates: SaaS providers update the software. Ensuring users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
- Scalability: SaaS applications can scale to accommodate growing user bases or increased usage.
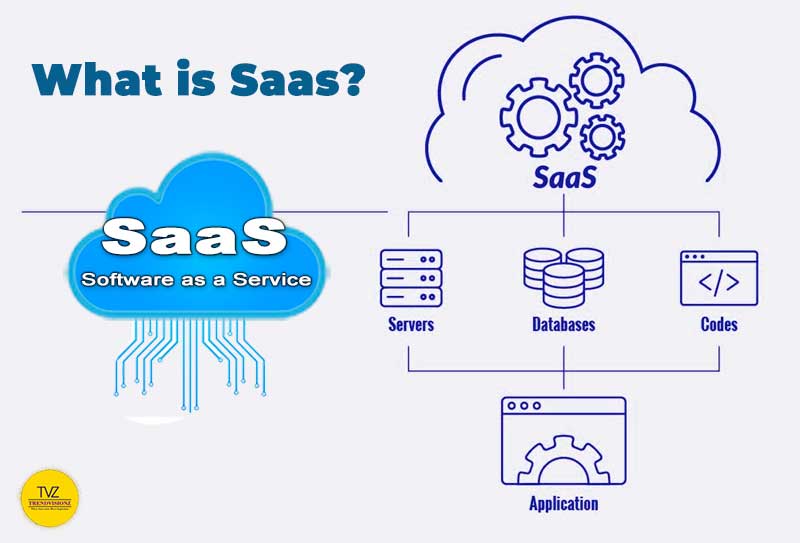
Benefits:
- Cost-effective: SaaS removes the need for initial software and hardware purchases.
- Easy deployment: SaaS applications can used quickly, often with a few clicks.
- Accessibility: SaaS apps are available to users at any time and from any location.
- Automatic updates: SaaS providers handle updates and maintenance. Reducing the burden on IT teams.
Drawbacks:
- Dependency on provider: Users rely on the SaaS provider for availability and performance.
- Limited customization: SaaS applications may offer a different level of customization. In comparision to on-premise software.
Uses:
- Customer relationship management (CRM). SaaS CRM solutions like Salesforce offer businesses a way to manage customer relationships.
- Email and collaboration. Tools like Google Workspace provide businesses with communication and productivity tools.
- Accounting and finance. SaaS software like QuickBooks Online offers businesses a way to manage their finances.
Providers of Software as a Service (SaaS) include BigCommerce and GoToMeeting, Dropbox, Salesforce, ZenDesk, Cisco WebEx, and Google Apps. These suppliers provide a variety of Internet-accessible apps for both individuals and organizations, all of which require a membership. Examples of cloud computing applications include web-based email services like Gmail, file storage services like Google Drive, and productivity suites like Microsoft Office 365.
Function as a Service (FaaS)
Also known as serverless computing. FaaS is a cloud computing model. Developers write and deploy code that triggers by specific events.
In this model, the cloud provider manages the infrastructure, scaling resources as needed. Billing of users is on the actual execution time of the functions. Making FaaS a cost-effective option.
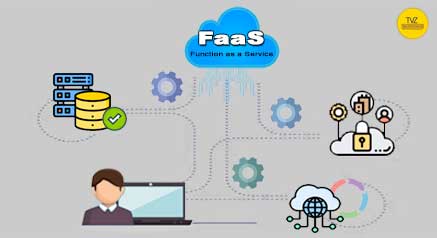
With FaaS, developers can focus on writing code. Without worrying about managing servers, leading to faster development cycles.
Examples of FaaS providers include AWS Lambda, and Azure Functions. Besides Google Cloud Functions, and IBM Cloud Functions.
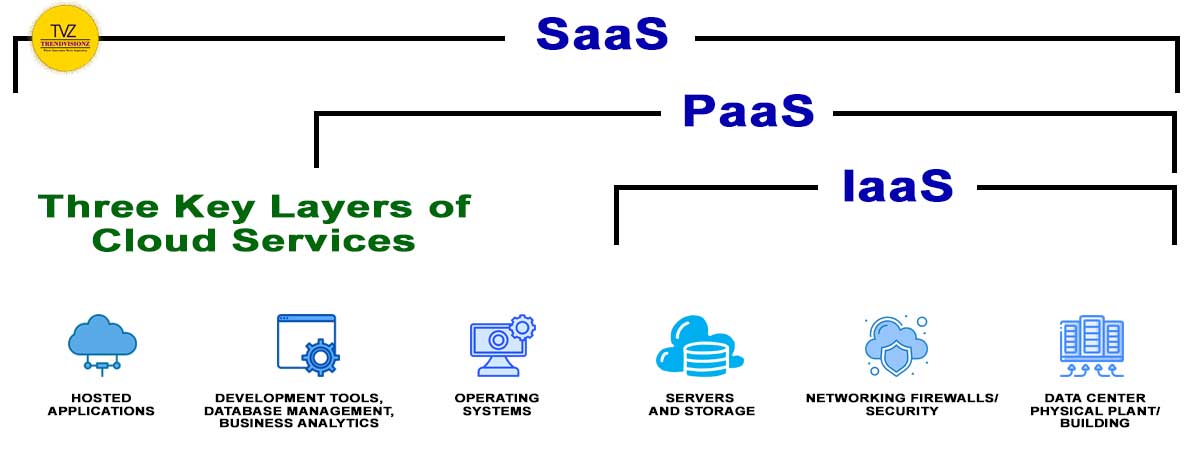
Navigating the Cloud: A Comparison of Service Models
The cloud computing revolution has opened new doors for businesses of all sizes. Offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. But, navigating the different service models can be confusing. This guide provides a clear comparison of the types of cloud services models. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Understand the key features, benefits, and drawbacks of each models. You can make an informed decision on types of cloud services models that aligns with your specific needs.
Difference between IAAS, PAAS and SAAS
Comparitive Analysis of three types of cloud services models
| S. No | Aspect | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Level of Control and Customization | • Provides the highest level of control and customization. • Ideal for system administrators and network architects. | • Provides a reasonable amount of control • Suitable for developers and application teams. | • Minimal control and customization. • Suited for non-technical users. | |
| Cost Structure | • Pay-as-you-go model based on resource usage (compute, storage, etc.). • Can be cost-effective for specific workloads. | • Typically priced based on the number of users or application instances. • Economical for development and testing environments. | • Subscription-based pricing. • Predictable costs but less flexibility. | |
| Security Considerations | • Users have control over security configurations. Responsible for securing their virtual machines and applications. • Requires expertise in security practices. | • Security managed by the PaaS provider. • Users focus on securing their applications. • Limited control over underlying infrastructure security. | • Security handled entirely by the SaaS provider. • Users trust the provider’s security measures. • No direct control over security settings. | |
| Management Responsibility | • Users manage infrastructure components (virtual machines, networks, etc.). • OS patching, backups, and monitoring are user responsibilities. | • PaaS provider manages infrastructure (servers, databases, etc.). • Users focus on application development and deployment. | • SaaS provider handles all aspects, including infrastructure, updates, and maintenance. • Users only interact with the software. | |
| Suitable Use Cases | • Custom applications requiring specific configurations. • Scalable web applications. • DevOps environments. | • Web and mobile app development.API development. • Database management. | • Email services. • Customer relationship management (CRM) software. • Collaboration tools (e.g., Google Workspace, Microsoft 365). |
Choosing the Right Model: Your Path to Cloud Success
The table provides a concise overview of differences between types of cloud services models.
- IaaS. Ideal for businesses that want to have high control over their applications & infrastructure. It also requires them to manage and maintain the servers.
- PaaS. Suitable for those who want to focus on application development. Without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure.
- SaaS. Perfect for businesses looking for ready-to-use applications. With no concerns about infrastructure or platform management.

The best choice for your types of cloud services depends on your specific requirements and budget. When you are about to take a decision, take into account following factors:
- Control and customization. How much control do you need over your infrastructure and applications?
- Technical expertise. Do you have an in-house IT team to manage the cloud platforms environment?
- Scalability. Do you need the flexibility to scale your resources up or down ?
- Security. What are your security requirements. And how comfortable are you entrusting data to a cloud provider?
By evaluating these factors and leveraging the insights provided in this comparison between types of cloud services. You can choose the cloud service model. One that unlocks the full potential of the cloud for your business.
The Future of Business: Cloud Computing Trends to Watch
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, cloud computing is at the forefront. Types of cloud services are shaping the future of business operations. With its ability to offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern business strategies. We will explore some key trends in cloud computing that are shaping the future of business.

Trends to Look Out For:
- AI and Machine Learning. The integration is enabling businesses to leverage data insights. For smarter decision-making and enhanced customer experiences.
- Expansion of Cloud Services. Cloud providers are expanding their services and solutions. To meet the evolving needs of industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
- Growing Emphasis on Cloud Security. Businesses are implementing robust security measures. To protect their data and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies. Many businesses are adopting multi-cloud strategies. To avoid vendor lock-in, optimize performance, and enhance resilience.
- Edge Computing. Enabling data processing closer to the source, reducing latency, and improving efficiency. For IoT devices and real-time applications.
- Serverless Computing. Allowing businesses to focus on writing code without managing server infrastructure. Resulting in further cost savings and better agility.
- Sustainability and Green Computing. Businesses looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprint. And adopt more environmentally friendly practices.
These trends highlight the dynamic nature of cloud computing. And its role in shaping the future of business operations.
The Evolution of Cloud Computing: A Blueprint for Future Business Success
Gain insights into the best practices and successful case studies. Harness the power of cloud computing to drive innovation and growth in business. Up to now, we have understood the diverse types of cloud services. Let’s now delve into how they can optimize efficiency and scalability in operations. Leveraging cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Netflix: Cloud Migration Journey
Netflix is one of the largest cloud computing users globally, utilizing it to power its streaming service for over 238.3 million subscribers across 190 countries. In 2023, Netflix generated $33.7 billion in revenue.
Netflix’s adoption of cloud computing has revolutionized its operations. The company transitioned to Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2008. Netflix saw a 20% increase in performance. Reduce its costs by using AWS’s pay-as-you-go pricing.

Netflix’s “The Crown” faced COVID-19 challenges during post-production. With a cloud-based workflow on AWS.. 10 artists completed over 600 VFX shots for the 10-episode season in 8 months. They all were working remotely.
With the new Amazon EC2 G5 instances, we can provision higher-end graphics workstations that offer up to 3x higher performance compared to workstations with EC2 G4dn instances. With G5 instances, content creators have the freedom to create more complex and realistic content for our viewers.
Stephen Kowalski, Director of Digital Production Infrastructure Engineering, Netflix
Benefits of Cloud Migration
- Scalability for fluctuating demands.
- Global expansion needs physical infrastructure.
- Cost optimization through pay-as-you-go model.
- Agile development and innovation.
- Enhanced resilience and disaster recovery.
Netflix’s cloud migration exemplifies the transformative impact of cloud computing on businesses.
Spotify: Harmonizing Innovation with Google Cloud
Spotify was launched in 23rd April, 2006. It provides access to a vast library of digital audio content, including over 100 million songs and five million podcasts. This content is sourced from record labels and media companies. Spotify stands as one of the largest music streaming service providers. Boasting over 602 million monthly active users, of which 236 million are paying subscribers.

Google Cloud supports Spotify’s diversification and success. Together, in 2016, they moved 1200 services and 20,000 daily job executions to the cloud.

Google Cloud removes a lot of the operational complexity from our ecosystem. We can iterate quicker on key needs. Having infrastructure managed for us streamlines our ability. To concentrate on what’s important to our users. And give them the experiences they know and love about Spotify.
Tyson Singer, VP of Technology and Platforms, Spotify
Spotify and Google Cloud move optimized its tech stack. And accelerated innovation for its vast user base.
- Cost Reduction: Achieved 60% cost reduction using Google Cloud’s cost-effective pricing.
- Scalability: GCP facilitated the scaling of services and data processing, enhancing user experience.
- Innovation Acceleration. Faster innovation with improved tech stack, leveraging machine learning and data processing tools.
- Operational Efficiency. Google Cloud’s automated, developer-friendly services. Streamlined operations, allowing focus on core business and user needs.
- Effective Data Use. Utilized BigQuery, Pub/Sub, and Dataflow for data analysis. And improved customer experiences while ensuring privacy.
Having evaluated the potential outcomes, we decided on the third option, an ‘all-in’ move to just one provider where we could build a deeper working relationship that went beyond simply offloading infrastructure to a third party. This led us to commit to the Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Niklas Gustavsson, Chief Architect, VP of Engineering, Spotify
The migration’s narrative from Chief Architect, highlights how it empowers engineers to concentrate on enhancing the audio experience for customers. Spotify’s success story with Google Cloud highlights the benefits of cloud migration. Spotify prioritizes the continuous evolution of Cloud Platforms. Ensuring seamless updates and improvements. To enhance user experience and stay ahead in the dynamic music streaming industry. Spotify’s premium subscribers grew by 29%, showcasing the impact of positive user experiences.
Coca-Cola Uses Microsoft Azure to Cut Costs
Coca-Cola is a total beverage company, providing over 500 brands across 200+ countries and territories. The company leverages Microsoft Azure’s cloud platforms to reduce IT costs and drive innovation. Benefiting from its scalability, security, and innovative features.

Although Coca-Cola primarily relies on Microsoft cloud technologies, we use an appropriate mix of other cloud providers to maintain solution diversity
Scott Leith, VP of global external and financial communications, The Coca-Cola Company

The new CONA platform efficiently manages 160,000 orders daily, generating $21 billion in annual net sales value.
- Cost Reduction: Utilizes Azure’s pay-as-you-go pricing model to reduce IT expenses.
- Scalability: Easily adds or removes resources to accommodate growth.
- Security: Relies on Azure’s secure features for global data protection.
- Innovation: Utilizes Azure’s machine learning. And AI tools to develop new products and services.
Examples include Coca-Cola UNITED using Azure for inventory management. Coca-Cola Freestyle for personalized customer experiences. And Coca-Cola Racing for performance optimization.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices: Cloud Migration Success
Cloud migration can be transformative, as demonstrated by Netflix, Spotify, and Coca-Cola. Here are key takeaways:
- Choose the right cloud partner: Consider factors like cost, scalability, security, and innovation capabilities.
- Start small and scale gradually: Begin with non-critical applications and migrate in phases.
- Leverage cloud-native features: Utilize services like machine learning, data analytics, and automated workflows.
- Focus on core business: Delegate infrastructure management to the cloud provider, freeing up resources for innovation.
It’s obvious that cloud computing will keep being a major factor. Determining how businesses operate in the future. Cloud computing is the way of the future for business. And those who can innovate and adapt will prosper in the digital economy.
Also Read:
- Smart Vehicle Choices: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing EV vs Hybrid
- What is Gen AI: Decoding The Ultimate Future of Marketing Creativity
- Co-Working Spaces: The New Hotspots for Freelancers and Remote Workers
FAQ: Types of Cloud Services
Is cloud computing secure?
Cloud security is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the user. Cloud providers put in place robust security measures. To protect their data centers and infrastructure. But, users are also responsible for securing their data. And applications within the cloud environment. Here are some key considerations: Choose a reputable cloud provider, Install strong security practices, Stay informed and vigilant
How do businesses choose the right cloud computing model?
Businesses should consider factors like their objectives, IT skills, security requirements. Also budget and workload nature. And compliance needs when choosing a cloud computing model.
Conclusion
In today’s digital age, understanding the various types of cloud services is crucial. Businesses must seek to capitalize on the benefits of cloud computing platforms. Important to understand: What is a cloud? A cloud is a virtual space for storing and accessing data remotely. From IaaS to SaaS and PaaS, each model offers unique advantages. In terms of scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility.
Examples of cloud computing revolutionize business operations. By embracing cloud technology, businesses can streamline operations, improve collaboration, and drive innovation. As cloud computing platforms continues to evolve. Stay informed about the latest trends. And explaining the cloud will be essential for businesses seeking to stay ahead of the curve.
The future of business lies in the cloud. And those who adapt and innovate will thrive in the digital economy. Embracing cloud technology is not a trend. But a necessity for businesses looking to succeed. In the fast-paced and ever-changing world of technology.
Call to Action:
Be aware of the digital age. Start your cloud journey today! Explore our website to learn more about our cloud services and how we can help your business thrive.
Share your Review
Our Digital Imprints:
About the Author: Anuj Mahajan is a Mass Communication Specialist, ICF Certified Coach & Corporate Trainer. Motivational Speaker / NLP Lifecoach. With expertise spanning filmmaking, business coaching, motivational speaking, blog writing, and authoring, he embodies versatility and mastery across diverse fields.
Chief Operating Officer: Nuteq Entertainment Pvt Ltd, and Co-Founder: Trendvisionz – A Premier Digital Marketing Agency in India
Get Connected to us with our Newsletters- Transforming Lives… Creating the magic. Just – Believe ~ Practice ~ Perform BizTech Chronicle… Navigating Tomorrow’s Tech Frontiers 🚀
Join my LinkedIn Group: Digital Marketing, Content Creation World Group
Follow me on Twitter or LinkedIn. Check out my website.