In recent times, Northern India has witnessed a series of deadly cloudbursts in India that turned valleys into disaster zones. Massive downpours triggered flash floods and landslides, killing hundreds and destroying homes, roads, and farmland. These back-to-back disasters dominated news channels and social media, painting a grim picture of Himalayan vulnerability.
At TrendVisionz, we bring research-driven analysis and expert insights to explain such extreme weather events. Research is our forte — through expert conversations, weather data, and field studies. My team and I uncover why cloudbursts are rising, the damage they cause, and the steps communities must take to prepare.

This article explores the causes of recent cloudbursts, their growing impact, and how preparedness can save lives. Studies show how such events occur, leading to sudden, intense rainfall in fragile terrains.
Join us as we gather the untold story of cloudbursts in Northern India.
Also Read:
- Citizenship by Investment and Residency: The Rise of Global Indians in 2025
- Fibre Insulation in Defence: The Backbone of India’s Modern Military Tech
What is a Cloudburst?
The widely accepted cloudburst definition. A sudden, extreme downpour in which more than 100 millimeters of rain1 falls in an hour over a very small area. Unlike normal rainfall, which is spread over longer periods and larger regions, a cloudburst is short, localized, and violent.
Ordinary rainfall allows ground and rivers to gradually soak in and carry the water away. A cloudburst can typically release nearly 72,300 tonnes of water over a single area within minutes. Triggering rapid surface runoff that quickly transforms into flash floods and landslides.
Studies show that steep Himalayan slopes intensify cloudburst effects2 due to orographic lifting, forcing moist air upward and triggering violent downpours that overwhelm valleys below. A climatological analysis3 found increasing occurrences of cloudburst-like events, signaling shifts in rainfall patterns in India
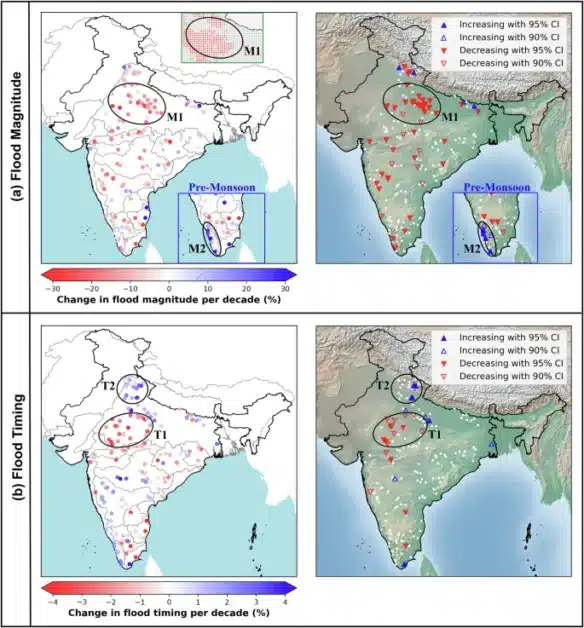
Experts and policymakers agree that tracking cloudbursts remains a major challenge. While the impact is visible in vulnerable states, reliable mapping is still missing. As Dr. Jitendra Singh, Minister of State for Science and Technology, replied to a question in Parliament:
“Cloud bursts are highly localized and are of very short duration. Most of the cloudbursts occur over very remote inaccessible sites in hilly region. Due to these reasons most of them remain unobserved and unreported and due to the lack of sufficient real-time data or information, cloudburst prone map for India is not available at present.”
Which regions face cloudbursts in India?
Cloudbursts are not evenly spread across the country. They strike most often in the Himalayas, where fragile slopes and unstable terrain magnify their destructive power. Recent incidents in 2025 highlight the worst-affected regions.
Jammu and Kashmir
During the Machail Mata Yatra on August 14, a massive cloudburst battered Chisoti village in Kishtwar, leaving destruction in its path. At least 67 people died, 300 were injured, and nearly 200 went missing. Just days later, on August 17, Kathua witnessed another cloudburst and landslip. Seven people were killed and several others injured, highlighting the back-to-back threats in the region.
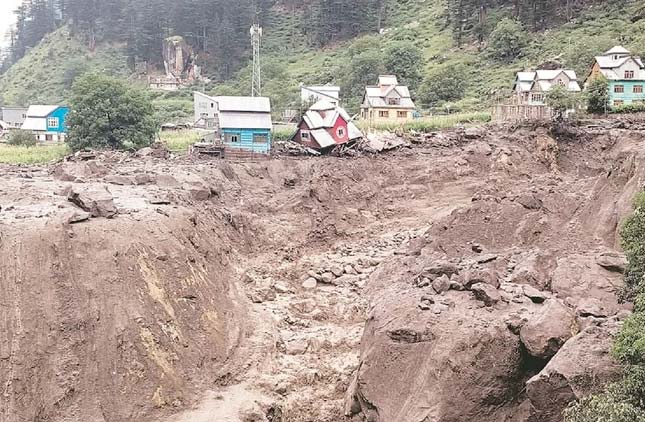

We were right there. suddenly there was a blast-like sound, and after that Cloudburst. We started to evacuate, but within 2 min, there was 4 feet of debris. We managed to rescue some, but others got trapped. My wife and daughter were trapped, but now they are safe- A Survivor
This is how a survivor recounts the terrifying moments. A reminder to us how swiftly cloudbursts turn lives upside down, leaving families clinging to hope.
Himachal Pradesh
In July, Himachal Pradesh reported ten cloudbursts and three flash floods in Mandi district. Thirteen deaths and 29 missing persons marked one of the state’s worst monsoon disasters in recent years.
Uttarakhand
On August 5, 2025, cloudbursts in Uttarkashi’s Kheer Ganga catchment and Sukhi Top unleashed massive flash floods. Dharali village saw homes, hotels, and markets swept away, with 4 confirmed deaths, 100 missing, and road access cut off. Livestock losses and Haridwar flooding worsened Uttarakhand’s crisis.
Ladakh
Cloudbursts on August 13, 2025, triggered flash floods across Lamayuru on the Srinagar–Leh Highway and Kargil’s Charkat Nallah. It disrupted traffic, damaging farmland, and raising concerns over flood control. Authorities launched restoration work, but local leaders have repeatedly voiced frustration over delays in implementing promised flood control measures.
In such life-threatening situations, departments must skip time-consuming processes like administrative approvals that can take two years. This project needs special focus now — 4,000 lives depend on it- Agha Ainul Huda, Councillor Parkachick
Such appeals highlight the urgency of action, reinforcing why preparedness against cloudbursts cannot be delayed. Cloudbursts in India follow a dangerous pattern in vulnerable Himalayan states. From cloud formation to sudden torrential downpour, each stage unleashes destruction with little warning. Understanding these stages is crucial to prepare for and reduce the risks of future disasters.
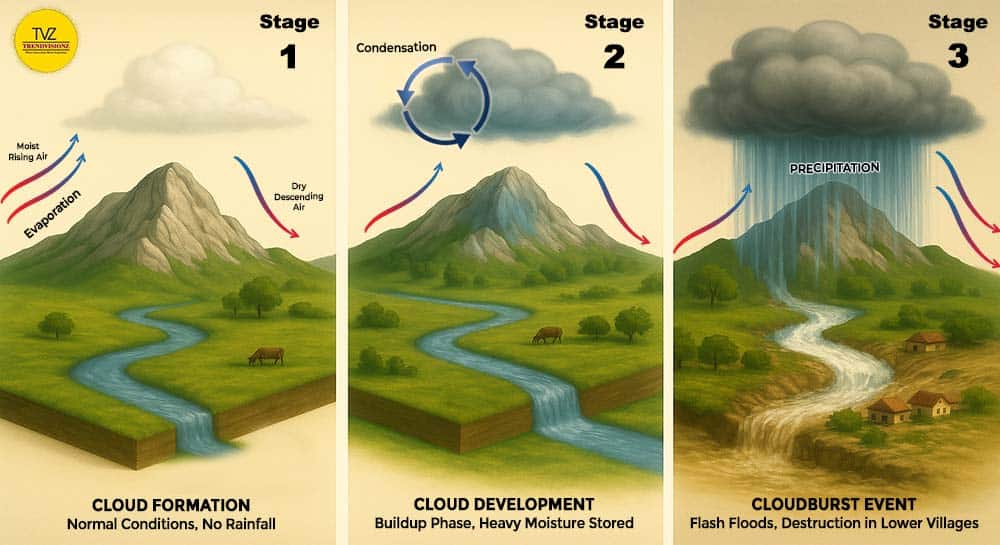
Stages of a Cloudburst
The Bay of Bengal sends moisture-rich winds that move westward and reach Northern India during the monsoon. When they meet cold mountain air in the Himalayas, destructive cloudbursts often follow.
- Stage 1: Cloud Formation. Clouds begin forming as warm, moist air rises along mountain slopes. This is the starting point of a cloudburst.
- Stage 2: Moisture Buildup. The clouds grow darker and heavier as they absorb more moisture. They now carry far more water than normal rainfall.
- Stage 3: Sudden Downpour. In minutes, the clouds release torrents of rain. Rivers overflow, villages flood, and destruction spreads rapidly across the valley.
Understanding these stages makes it easier to identify why cloudbursts are different from normal rainfall.
Orographic Lift and Cloudbursts
One of the main drivers of cloudbursts in India is orographic lift. It’s a process where moist air rises as it encounters steep mountain slopes. As the air ascends, it cools and condenses rapidly, forming dense clouds overloaded with moisture. When the buildup becomes unstable, sudden intense rainfall occurs within minutes, overwhelming valleys below. In the Himalayas, the sharp elevation changes amplify this effect.
Regions like Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir especially prone to cloudburst disasters. Understanding orographic lift helps explain why these events are concentrated in mountain regions and remain difficult to forecast. Watch the animated Youtube Video.
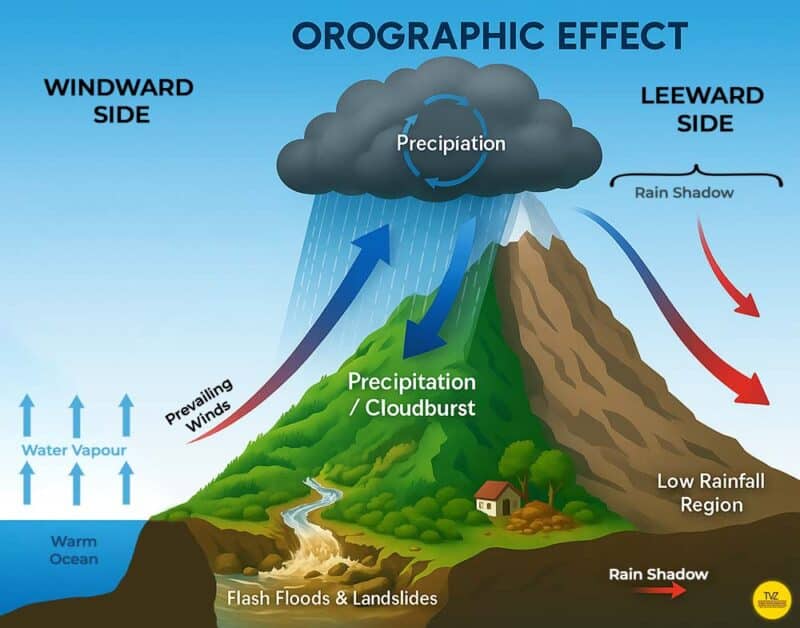
Do You know What is a Rain Shadow Area?
A rain shadow is a dry area on the leeward side of a mountain range.
👉 Example in India: The Deccan Plateau lies in the rain shadow of the Western Ghats. That’s why areas like interior Maharashtra and northern Karnataka are much drier than the west coast.
Key characteristics of a Cloudburst
Cloudbursts differ sharply from normal rainfall. Their intensity, speed, and impact make them among the most destructive weather events in India, especially in fragile Himalayan regions.
- Rainfall intensity: More than 100 mm per hour
- Duration: Short, usually minutes to an hour
- Area covered: Localized, often less than 30 square kilometers
- Immediate risks: Flash floods in the Himalayas, landslides, damaged houses, and loss of lives
A cloudburst is not simply rain. It is a violent natural disaster that leaves little time for warning or response, making preparedness critical in Northern India’s fragile terrain.
Impact of Recent Cloudbursts in India
Cloudbursts are among the most destructive monsoon disasters. The recent cloudburst events in 2025 across Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, and Himachal Pradesh resulted in widespread fatalities, mass displacement, and severe economic loss. As per IMD, the Himalayan belt remains the most vulnerable to such extreme rainfall.
Human Impact
Cloudbursts strike suddenly, leaving little time to escape. The consequences are visible in lives lost, displacement of communities, and the lasting psychological trauma that survivors endure.
- Dozens to hundreds of deaths in single events (Kishtwar, 2025: 67 confirmed)
- Over 300 injured in Jammu & Kashmir incidents (State Disaster Reports)
- 200+ people missing after flash floods in Himachal Pradesh
- Entire families displaced, forced into temporary shelters
- Survivors face trauma, anxiety, and long-term mental health challenges
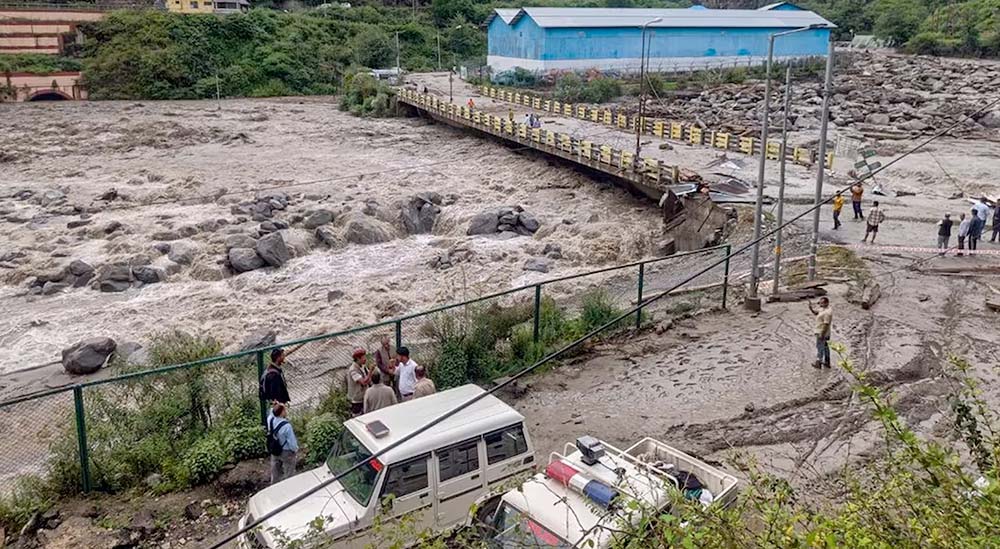

Environmental and Infrastructure Damage
Beyond immediate casualties, cloudbursts reshape landscapes and destroy vital infrastructure. The fragile Himalayan ecosystem suffers long-lasting scars.
- Flash floods sweep away villages and farmland (NDMA)
- Landslides block highways, delaying rescue operations
- Soil saturation causes land subsidence, destabilizing terrain
- Bridges and roads worth ₹120 crore destroyed in Himachal Pradesh (SDMA 2025)
- Wildlife habitats and forests disrupted by silt and debris
Even national leaders raised concern, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s tweet drawing attention to the urgency of cloudburst preparedness.
Societal and Economic Consequences
The aftermath of cloudbursts cripples local economies and creates social instability. Farming, tourism, and livelihoods collapse, while rehabilitation demands strain government resources.
- Agricultural losses worth hundreds of crores every year
- Tourism revenue collapses as pilgrimages and bookings are cancelled
- Local businesses destroyed, forcing migration to cities
- Relief and rehabilitation costs run into thousands of crores (NDMA)
- Survivors report PTSD, fear, and reduced resilience in communities
The impact of recent cloudbursts in India cannot be measured only in statistics. These disasters alter lives, damage ecosystems, and weaken economies. Understanding their human, environmental, and social costs is vital for building resilience in Himalayan regions.
Disaster Preparedness and Lessons
The lessons from recent cloudburst events in Northern India highlight the urgent need for preparedness. While cloudbursts cannot be prevented, their impact can be reduced through better forecasting, stronger infrastructure, and community-driven resilience. According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), early warnings remain the most effective tool in saving lives. Research shows that machine learning models can improve cloudburst prediction4 by analyzing weather data and detecting early warning signals
Importance of Early Warnings
Timely forecasts and IMD weather warnings play a critical role in reducing casualties. In recent incidents, alerts issued in advance allowed authorities to suspend pilgrimages and evacuate vulnerable zones, preventing even greater tragedy. Expanding radar coverage in Himalayan regions remains a priority.
- Improved satellite tracking helps identify storm clusters.
- District-level dissemination ensures messages reach remote villages.
- Mobile-based alert systems are increasingly effective in high-risk zones.
Government Initiatives and Disaster Management
The Indian government has taken major steps to strengthen disaster preparedness in India. Focusing on early warning, rapid response, and community safety. Through the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), State Disaster Response Forces, and the IMD, efforts are directed toward safeguarding lives and property. As confirmed in a Parliamentary reply by the Ministry of Earth Sciences:
IMD plays a crucial role in safeguarding lives and property through its advanced observational network and forecasting systems, enabling timely preparedness and response in close collaboration with the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) – PIB Delhi, July 23, 2025
Through the efforts of key stakeholders, India’s government has reinforced disaster preparedness by developing modern early warning systems that integrate real-time satellite, radar, and surface data with advanced forecasting models. These systems deliver impact-based alerts to vulnerable regions, helping communities prepare more effectively for extreme weather events.
Key measures include:
- Installation of additional Automated Weather Stations (AWS), rain gauges, and Doppler Weather Radars (DWR) across states.
- Launch of a GIS-based Decision Support System (DSS) for real-time hazard monitoring and early warnings.
- Introduction of “Mission Mausam” to build a weather-ready and climate-smart nation.
Community Awareness and Individual Preparedness
Preparedness at the community and household level is equally vital. Awareness drives, school programs, and training sessions ensure people know what to do when disaster strikes.
Key steps individuals and communities can take include:
- Monitor IMD weather warnings and government-issued local advisories.
- Avoid riverbanks or low-lying areas during heavy rains.
- Identify safe zones and plan evacuation routes in advance.
- Keep emergency kits ready with food, water, and essential medicines.
- Support community resilience by participating in local preparedness programs.

The lessons from recent cloudbursts in India are clear: preparedness saves lives. By combining IMD’s forecasts, government initiatives, and community action, vulnerable regions can build resilience and reduce the devastation caused by sudden extreme rainfall.
Also Read:
- Dam Politics: Massive China Brahmaputra Dam Reshaping South Asia
- India Air Defence System: How Operation SINDOOR Redefined Modern Warfare
- The Secret Life of Sea Sponges: Nature’s Silent Architects of the Ocean
FAQ: Cloudbursts in India
What is the difference between a cloudburst and heavy rain?
A cloudburst is rainfall of over 100 mm in an hour in a small area, while heavy rain is more widespread and less intense. Cloudbursts usually cause flash floods and landslides.
Can cloudbursts be predicted?
Cloudbursts are difficult to predict precisely because they occur suddenly and locally. However, IMD weather warnings and satellite tracking can alert vulnerable regions about intense monsoon activity and potential extreme rainfall.
What role does orographic lift play in cloudbursts?
Orographic lift occurs when moist air rises over mountains, cools, and condenses rapidly. This leads to intense cloud formation and sudden rainfall. In the Himalayas, steep slopes amplify this effect, often triggering destructive cloudbursts with flash floods and landslides.
How does climate change affect cloudbursts?
Climate change is increasing cloudburst frequency in India. Rising temperatures cause higher moisture retention in the atmosphere, leading to stronger storms, intense rainfall, and frequent flash floods in Himalayan regions.
How to stay safe during cloudbursts?
Stay away from rivers and low-lying areas, follow official IMD weather warnings, and move to higher ground quickly. Keep an emergency kit ready and plan evacuation routes with your community to ensure safety.
Conclusion
The recent cloudbursts in India reveal how fragile Himalayan regions are to sudden extreme rainfall. From their meteorological causes to their devastating human and economic impact, these disasters highlight the urgency of preparedness.
Early IMD alerts, stronger infrastructure, and community awareness can save lives and reduce losses. Building resilience is no longer optional but essential for vulnerable states. Stay updated with IMD warnings and adopt local preparedness measures to stay safe.
At TrendVisionz, we remain committed to translating complex climate data into clear insights that help you stay informed and prepared
Additional Resource:
- Lohan, N., Routray, A., Kumar, R., Mahala, B. K., & Kumar, S. (2025). Validation and diagnostic study of cloudburst events over the Himalayan region using IMDAA and ERA5. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2024.2446589 ↩︎
- A.P. Dimri, A. Chevuturi, D. Niyogi, R.J. Thayyen, K. Ray, S.N. Tripathi, A.K. Pandey, U.C. Mohanty, Cloudbursts in Indian Himalayas: A review, Earth-Science Reviews, Volume 168, 2017, Pages 1-23, ISSN 0012-8252, ↩︎
- Akash Singh Raghuvanshi, Ricardo M. Trigo, Ankit Agarwal, Climatology of extreme precipitation spells induced by cloudburst-like events during the Indian Summer Monsoon, Journal of Hydrology X, Volume 26, 2025, 100197,
ISSN 2589-9155, ↩︎ - D. Karunanidy, P. S. Rakshith, G. Sireesha, N. M, M. N and M. Sreedevi, “Cloudburst Prediction in India Using Machine Learning,” 2023 6th International Conference on Recent Trends in Advance Computing (ICRTAC), Chennai, India, 2023, pp. 645-650, doi: 10.1109/ICRTAC59277.2023.10480754. ↩︎
Share your Review
About the Author: Anuj Mahajan is a Mass Communication Specialist, ICF Certified Coach & Corporate Trainer. Motivational Speaker / NLP Lifecoach. With expertise spanning filmmaking, business coaching, motivational speaking, blog writing, and authoring, he embodies versatility and mastery across diverse fields.
Chief Operating Officer: Nuteq Entertainment Pvt Ltd, and Co-Founder: Trendvisionz – A Premier Digital Marketing Agency in India
Get Connected to us with our Newsletters- Transforming Lives… Creating the magic. Just – Believe ~ Practice ~ Perform BizTech Chronicle… Navigating Tomorrow’s Tech Frontiers 🚀
Join my LinkedIn Group: Digital Marketing, Content Creation World Group
Follow me on Twitter or LinkedIn. Check out my website.
✍️ A Note from the Editor
At TrendVisionz, we craft each article with purpose—guided by research, passion, and the belief that storytelling can spark change. We’ve kept our content open and free for all, because we believe knowledge should never be behind a paywall.
But creating quality digital content takes time, heart, and resources. If this article resonated with you, we’d be deeply grateful for your support. Even $10/month can help us keep producing content that informs, empowers, and uplifts.
💛 Support our work: You can contribute directly via PayPal or email us at anujmahajan@trendvisionz.com to set up your monthly support.
Thank you for believing in independent digital journalism. —Editor






9 comments
[…] Posts Recent Cloudbursts in India — Causes and Preparedness Cervical Cancer Prevention in India: Screening and HPV Vaccination Nutrient Sequencing: A […]
[…] Posts Recent Cloudbursts in India — Causes and Preparedness Cervical Cancer Prevention in India: Screening and HPV Vaccination Nutrient Sequencing: A […]
Your blog is a testament to your dedication to your craft. Your commitment to excellence is evident in every aspect of your writing. Thank you for being such a positive influence in the online community.
I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will
This is such a valuable article! 👏 I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work! 🚀
A massage is a fantastic way to soothe sore muscles. It helps your body recover faster.
I have been browsing online more than three hours today yet I never found any interesting article like yours It is pretty worth enough for me In my view if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before
[…] Skincare Services Easy in the UAE How the Right Seating Can Improve Posture and Productivity Recent Cloudbursts in India — Causes and Preparedness Cervical Cancer Prevention in India: Screening and HPV […]
[…] Recent Cloudbursts in India — Causes and Preparedness […]
Comments are closed.