Diabetes and metabolic disorders continue to rise worldwide. India is often called the diabetes capital of the world, and the statistics back it. Over 77 million adults live with diabetes, while 25 million more are prediabetic, with alarming increases now seen among younger populations. This places an urgent need on finding simple, accessible lifestyle solutions. Not everyone can commit to rigorous workouts or constant activity, which is why researchers are exploring new ways to improve health during everyday routines. One such discovery is the Soleus Push-Up (SPU) — a simple seated heel raise designed to activate a deep calf muscle in a unique way.
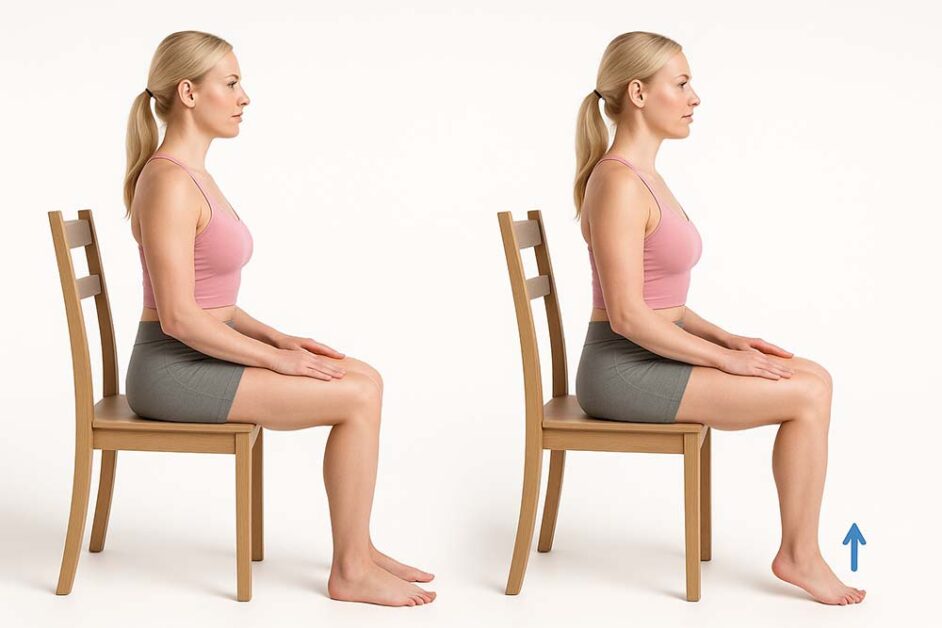
Backed by promising scientific studies, this small movement is drawing attention for its potential to influence blood sugar regulation and overall metabolic health.
At TrendVisionz, our experience working closely with leading healthcare professionals has shown us how important it is to bridge complex research with practical solutions. Could something as effortless as lifting your heels while sitting reshape the way we approach diabetes prevention and metabolic wellness? Let’s explore how this micro-movement could make a major impact.
Also Read:
- The Protein Market in India Is Exploding—Here’s What You Need to Know in 2025
- Magnesium Benefits for Women: A Lifelong Ally for Hormones, Bones, and Energy
What Makes the Soleus Push-Up Different?
The soleus is a powerful yet often overlooked muscle in the lower leg. Located beneath the gastrocnemius (the visible calf muscle), it plays a crucial role in posture and endurance, helping us stand and walk for long periods without fatigue. Unlike the “show” muscles, the soleus muscle activation taps into slow-twitch fibers designed for continuous work.
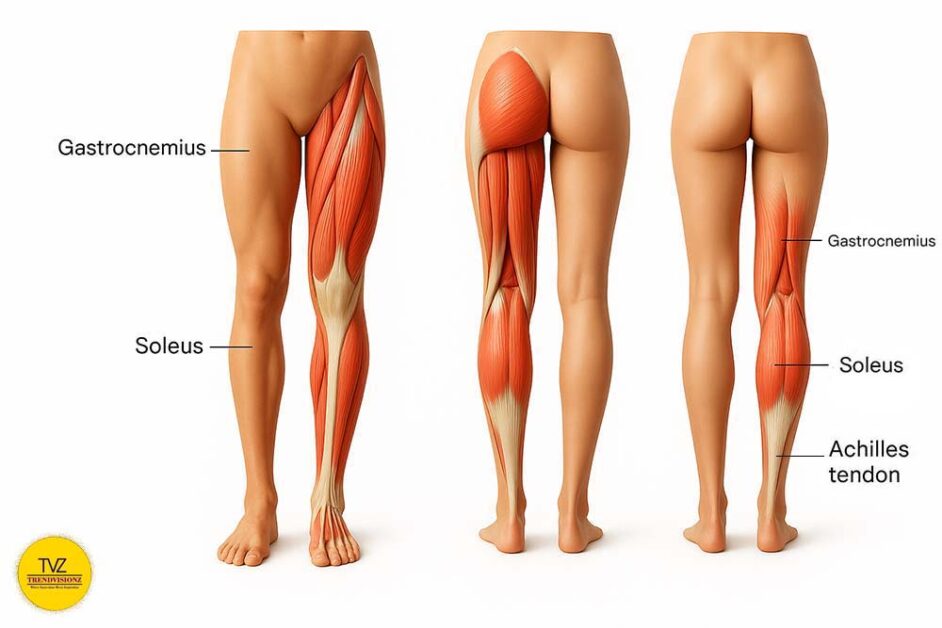
Traditional walking or a standing calf raise recruits the calf muscles but only briefly sparks metabolic change. In contrast, the soleus pushup exercise — a seated heel raise where the toes stay grounded and the heel lifts repeatedly — triggers a unique response. Unlike most movements, it keeps the soleus working in a steady rhythm.
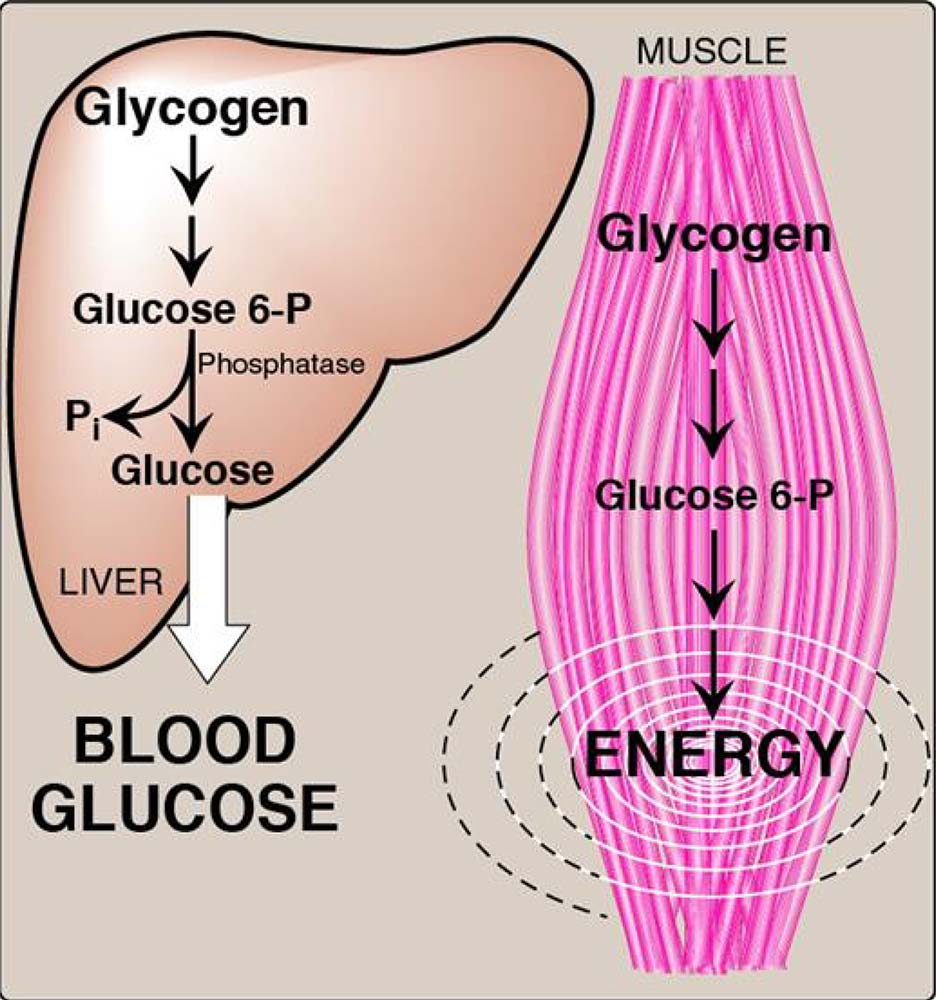
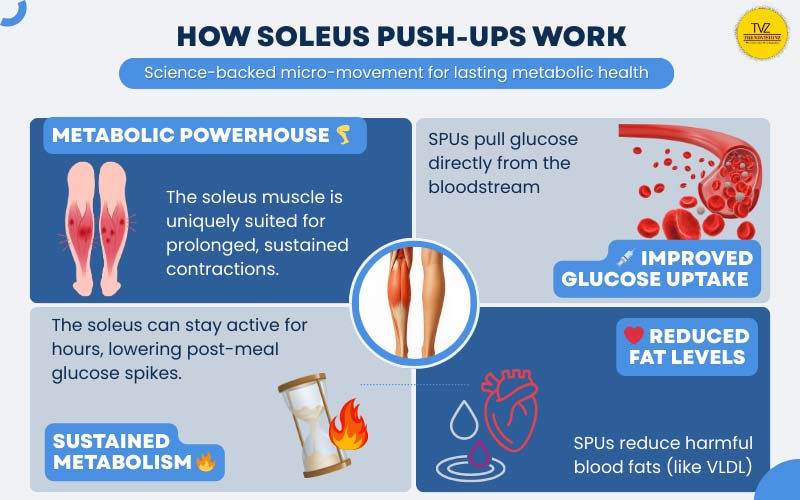
This constant engagement leads to sustained oxidative metabolism, a process where the muscle relies on blood glucose and fats for fuel rather than depleting glycogen stores. As a result, the seated calf raise exercise can burn glucose and fat efficiently for hours without tiring the muscle.
Why the Soleus Push-Up Stands Out:
- Activates a deep, endurance-based muscle rarely targeted in workouts.
- Works while sitting, making it accessible anywhere.
- Sustains oxidative metabolism for continuous glucose and fat use.
- Complements but doesn’t replace regular cardio or strength training.
Physicians recognize SPUs as uniquely effective, practical movements for improving blood sugar and fat metabolism.
If you keep doing it while you are sitting at your desk and if you can do it for at least 3–4 hours during the day, this has been shown to tremendously improve your glucose and triglycerides metabolism. – Dr. Arvind Bhateja, Lead Neurosurgeon, Sparsh Hospital
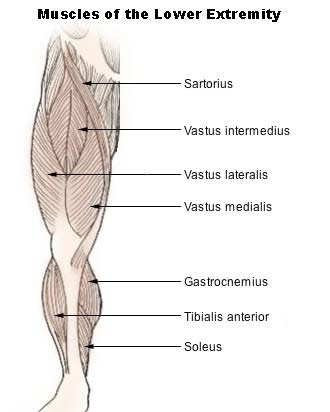
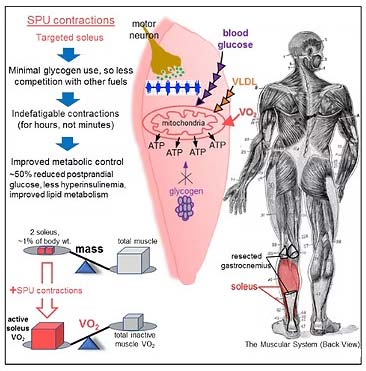
The image above shows where the soleus sits among lower leg muscles. The soleus pushup exercise differs from walking or calf raises because it uniquely sustains soleus muscle activation. This seated calf raise exercise taps into oxidative metabolism, helping burn glucose and fat efficiently for hours, even while sitting, with minimal fatigue.
Research Insights on Blood Sugar and Metabolism
A Lancet study revealed1 over 101 million Indians have diabetes, while 136 million are prediabetic—an alarming trend affecting professionals, teenagers, and seniors alike, demanding urgent lifestyle interventions.
The greatest attention around the soleus pushup benefits comes from recent peer-reviewed studies. At the University of Houston, Hamilton and colleagues (2022)2 reported that performing the Soleus Push-Up after consuming glucose reduced postprandial glucose levels by 52% and lowered insulin requirements by 60%. This suggests the soleus pushup diabetes connection may be clinically significant for managing spikes after meals.
A follow-up pilot by Elek et al. (2024)3 examined individuals with prediabetes. Their findings showed a 32% reduction in postprandial glucose excursions during an oral glucose tolerance test, even without lab-based guidance. This indicates the SPU could be a practical tool for people already at higher metabolic risk.
Unlike typical muscles, the soleus uses blood glucose directly, sparing glycogen for sustained metabolic activity.
What makes these outcomes unique is the underlying mechanism. Instead of relying on stored glycogen, the SPU directs the soleus to use circulating blood glucose and fatty acids as fuel. This glycogen-sparing action enables hours of sustained glucose metabolism without rapid fatigue — a rare quality for any exercise performed while sitting.
Key Research Takeaways
- Hamilton et al. (2022): 52% reduced glucose, 60% reduced insulin needs.
- Elek et al. (2024): 32% lower glucose response in prediabetic individuals.
- Mechanism: burns blood sugar and fats, sparing glycogen stores.
Takeaway: Studies confirm the soleus pushup benefits include lower blood sugar spikes, improved insulin sensitivity, and better glucose metabolism. Both healthy and prediabetic individuals show reduced postprandial glucose when practicing SPUs, making them a promising tool for metabolic health.
What Are the Soleus Pushup Benefits for Blood Sugar and Metabolism?
The soleus pushup exercise is gaining attention for its role in improving glucose regulation and overall metabolic health. Backed by clinical studies, the soleus pushup benefits extend well beyond simple movement — offering a science-backed solution for those concerned about blood sugar and diabetes.
Key Benefits
- Improved blood sugar control – Practicing SPUs helps the body clear glucose more efficiently from the bloodstream, reducing spikes after meals.
- Better insulin response – Soleus activation boosts energy expenditure without relying on larger muscle groups, making it effective even for sedentary individuals.
- Supports long sitting hours – Office workers, students, and older adults can integrate SPUs into their routine without needing special equipment or gym time.
For people with prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes, the soleus pushup diabetes connection is especially promising. While not a replacement for medical treatment, it serves as a safe, low-impact addition to lifestyle management under professional guidance.
Takeaway: The soleus pushup exercise is more than a seated heel raise — it’s a metabolic tool proven to lower blood sugar, improve insulin sensitivity, and support long-term wellness.
Beyond Sugar – Other Health Benefits
While the most discussed impact of the Soleus Push-Up is blood sugar control, researchers have also noted broader effects on overall metabolic health. Beyond the proven role of the soleus pushup blood sugar regulation effect, SPUs also contribute to fat metabolism and cardiovascular health
By stimulating the soleus muscle, the body shifts into a state that accelerates lipid use, lowering triglycerides and supporting long-term cardiovascular function. This makes the SPU not only a glucose regulator but also a practical fat burning exercise.
Over time, these combined effects may play a role in diabetes prevention and reducing the risk of heart disease. Elevated triglycerides and insulin resistance are two critical drivers of metabolic syndrome, and the Soleus Push-Up offers a simple way to counter both. For sedentary workers, office professionals, or elderly individuals who cannot engage in vigorous exercise, SPUs present a safe, seated option that delivers meaningful benefits.
Key Health Benefits:
- Enhances fat metabolism and reduces triglyceride levels
- Supports cardiovascular wellness and weight management
- Contributes to diabetes prevention strategies
- Accessible for sedentary or mobility-limited individuals
Takeaway:
Soleus Push-Ups are more than a blood sugar tool. This fat burning exercise lowers triglycerides, supports heart health, and improves overall metabolic health. For sedentary workers and elderly adults, it offers a practical step toward diabetes prevention and wellness.
How to Perform the Soleus Push-Up Safely
The Soleus Push-Up is designed to be simple and accessible, yet its benefits for blood sugar control and metabolic health depend on proper form. Performed correctly, this micro-movement exercise engages the soleus muscle without strain, making it a safe addition to any seated workout routine.
Step-by-step guide:
- Sit upright in a chair with your feet flat on the ground.
- Keep the front of your foot and toes firmly planted.
- Lift your heels as high as possible, pressing through the balls of your feet.
- Slowly lower your heels back to the floor.
- Repeat continuously at a steady rhythm for several minutes.

To maximize effectiveness, aim to practice after meals when blood sugar levels naturally rise. SPUs can also be performed while working at a desk, watching television, or reading, allowing consistent activation without interrupting daily life. The key is repetition and rhythm, ensuring the soleus muscle remains engaged long enough to trigger sustained energy use.
Because this is a low-impact seated workout, most people will find it comfortable. However, individuals with advanced diabetes, circulation issues, or musculoskeletal conditions should consult their doctor before incorporating SPUs into a routine.
Watch Dr. Marc Hamilton, developer of Soleus Push-Ups (SPUs), explain the technique and its metabolic benefits. This physician-led lessons will help you improve everyday health.
Practical tips:
- SPUs cut post-meal glucose spikes by over half.
- Technique uses body weight, no external equipment needed.
- Soleus activation sustains fat and glucose metabolism longer.
- Smooth ankle motion, not typical calf raises, ensures results.
- Consistency matters more than speed—practice daily while sitting.
Takeaway
The Soleus Push-Up is an easy micro-movement exercise. By lifting heels while seated, you activate the soleus muscle, support blood sugar control, and build muscle endurance. Safe and effective, SPUs fit naturally into everyday routines for lasting health benefits.
Should You Add SPUs to Your Routine?
The evidence from each soleus pushup study suggests that this movement has significant potential for improving blood sugar control and overall metabolic health. But should it be part of your daily routine?
SPUs appear especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes, prediabetes, or those at risk due to sedentary lifestyles. Office workers who spend long hours seated, older adults with mobility limitations, or anyone looking for a low-impact complement to their current regimen may find SPUs a practical choice.
In a world that often glorifies extremes—extreme food habits, extreme workouts, extreme results—the soleus push-up reminds us that the body responds not just to how hard we push it, but to how intelligently we engage with it.– Luke Coutinho, Holistic Lifestyle Coach in Integrative Medicine
This aligns perfectly with the Soleus Push-Up philosophy: sustainable, intelligent activation of a single muscle that creates measurable health benefits without intensity or extremes. That said, it is important to note the limitations. The Soleus Push-Up is not a substitute for walking, strength training, or aerobic exercise. While it offers unique metabolic advantages, long-term health still depends on a mix of activity, balanced nutrition, and medical care when necessary.
Looking forward, SPUs may represent the beginning of a broader focus on micro-movement exercises in preventive health. By harnessing small, sustainable movements that fit into daily life, researchers hope to give people more tools for managing chronic conditions and improving quality of life without overwhelming lifestyle changes.
Key Considerations:
- Best suited for diabetics, prediabetics, sedentary workers, and elderly individuals
- Complements but does not replace full-body workouts
- Represents the future of micro-movement strategies in healthcare
Takeaways: Each soleus pushup study shows real benefits for blood sugar control and metabolic health. While not a substitute for exercise, SPUs are a practical addition to daily routines, offering safe support for diabetics, prediabetics, and sedentary individuals alike.
Also Read:
- Cervical Cancer Prevention in India: Screening and HPV Vaccination
- Nutrient Sequencing: A Smarter Way to Eat for Energy, Focus, and Health
FAQ:Soleus Push-Up
How many Soleus Push-Ups should I do per day?
Do about 50 soleus push-ups per minute for 3–4 hours daily if targeting blood sugar control. For strength, begin with 3–5 sets of 12–20 reps. Focus on consistency, gradual progress, and comfort instead of chasing high numbers.
Does the Soleus Push-Up really work?
Yes. Research shows Soleus Push-Ups reduce post-meal blood sugar spikes, improve insulin sensitivity, and boost fat metabolism. Studies from the University of Houston and follow-ups in prediabetics confirm measurable benefits for metabolic health.
Why is the soleus called the second heart?
The soleus helps pump blood back to the heart from the legs during standing and sitting. Its endurance-based action supports circulation, earning it the nickname “second heart” in medical and fitness literature.
Conclusion
The Soleus Push-Up is a simple seated move with powerful benefits. Incorporating the soleus pushup blood sugar regulation move into daily life can be a simple yet effective way to support long-term wellness. Backed by credible studies, this micro-movement exercise is safe, accessible, and effective for most people.
If you’re diabetic or prediabetic, consult your doctor before adding SPUs to your routine. For everyone else, try practicing them after meals or during work breaks. Small, consistent steps can make a big difference. Explore more practical health insights and guides with us at TrendVisionz, where knowledge meets everyday wellness.
Additional Resource:
- Metabolic non-communicable disease health report of India: the ICMR-INDIAB national cross-sectional study (ICMR-INDIAB-17) Anjana, Ranjit MohanMohan, Viswanathan et al. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, Volume 11, Issue 7, 474 – 489 ↩︎
- Hamilton MT, Hamilton DG, Zderic TW. A potent physiological method to magnify and sustain soleus oxidative metabolism improves glucose and lipid regulation. iScience. 2022 Aug 5;25(9):104869. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104869. PMID: 36034224; PMCID: PMC9404652. ↩︎
- Elek, David & Melczer, Csaba & Tóth, Miklós & Sonkodi, Balazs & Acs, Pongrac & Kovacs, Gabor. (2024). The effects of soleus push up on glucose tolerance among individuals with prediabetes. 10.1101/2024.11.14.623602. ↩︎
Stay Connected with Me:
Anuj Mahajan is a Mass Communication Specialist, ICF-ACC Certified Coach, Corporate Trainer, Motivational Speaker, NLP Life Coach, Filmmaker, and Author. With 30+ years in media, marketing, and leadership coaching, he unites storytelling, mindfulness, and digital transformation.
- Explore my work: Nuteq Entertainment | TrendVisionz | Author Profile
- Read our newsletters: Transforming Lives | BizTech Chronicle | Nuteq Newsline
- Guest writer: BizCatalyst360 | Praja Today
- Books: Go Mindfulness: Practices for Professionals Coached
- Join the community: LinkedIn Group – Digital Marketing & Content Creation World
- Connect with me: LinkedIn | Twitter | #StoryforBusiness
- Share your review: Leave your review on Google — your feedback helps us grow.
Believe. Practice. Perform. Let’s create impact together.
✍️ A Note from the Editor
Independent storytelling thrives with you. Contribute $15/month via PayPal or email us at anujmahajan@trendvisionz.com. [Guest write for us — Free or Paid.]
Health Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new exercise, especially if you have diabetes, circulation issues, or other medical conditions.

